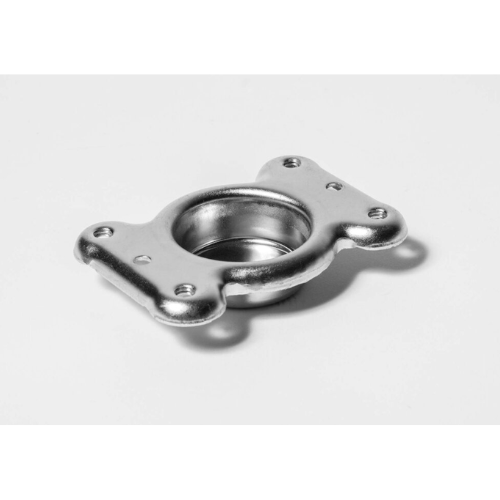
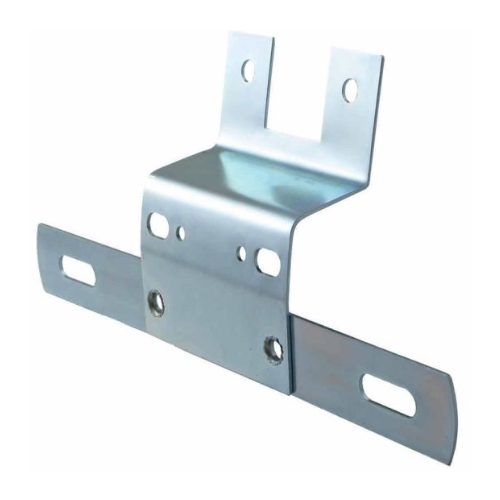
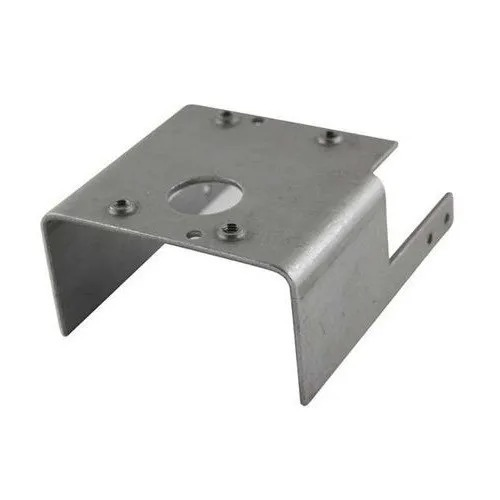
Metal Stamping Services
Discover the power of precision with Frigate’s metal stamping services. From machinery components to operational essentials, our expert team delivers quality results swiftly and affordably. Experience the efficiency of sheet metal shaping with Frigate.

What We Do
Our Metal Stamping Offerings
We create complex, high-quality parts from a variety of materials with our precision metal stamping skills, utilizing state-of-the-art tools and techniques to guarantee superior quality.
Get Your Quote Now
- Instant Quotation
- On-Time Delivery
- Affordable Cost
Advance expertise with exceptional delivery
Progressive Stamping Excellence at Frigate
Frigate proudly offers stamping services with complex parts from certified vendors, specializing in Progressive dies. These dies are adeptly fed from a steel coil, starting with a coil reel for unwinding, followed by a straightener to level the coil, and then into a feeder, which advances the material vendors’ parts into the press and die at a predetermined feed length. The number of stations in the die can be determined depending on the part’s complexity.
Our stamping process involves placing flat sheet metal in either blank or coil form into a stamping press, where a tool and die surface form the metal into a net shape. This comprehensive process includes various sheet-metal forming manufacturing techniques, such as punching using a machine or stamping press, blanking, embossing, bending, flanging, and coining.
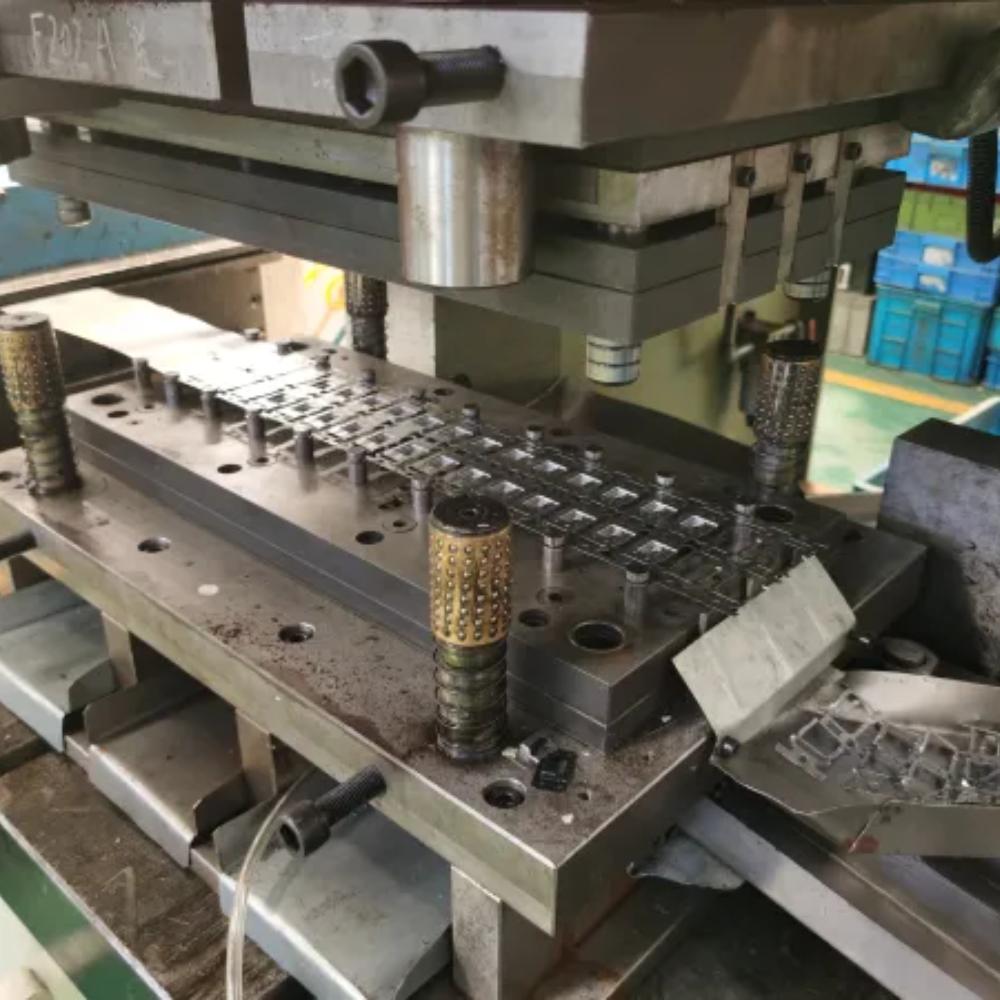
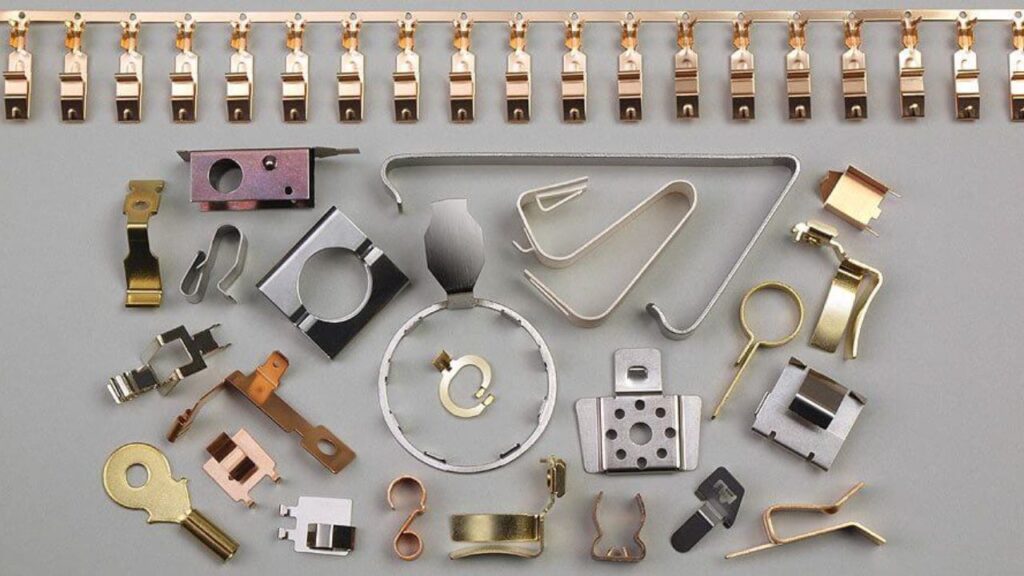


Stamping services utilize progressive dies for high-precision, high-volume production.
Our Clients





























Our Business Verticals
Defense
Aerospace
Electrical
Automotive
Mining
New Energy
Healthcare
Agricultural
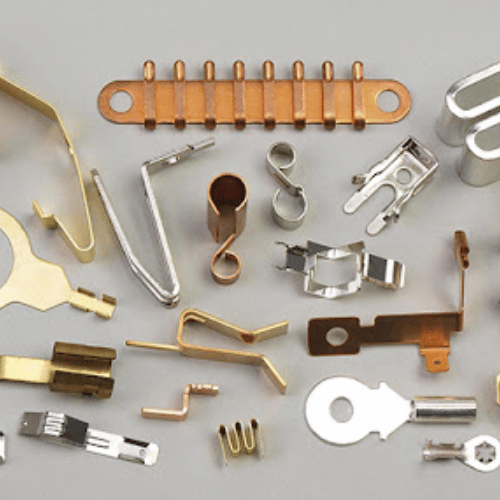
Metal Stamping Materials
Frigate offers a variety of materials for both standard and custom metal stampings,
Popular options include CRS steel like 1008, 1010, or 1018, known for its cold forming capabilities.
Choices like 301, 304, and 316/316L offer varying degrees of tensile strength and corrosion resistance, with 316/316L providing the highest corrosion resistance.
Options include C110, prized for its conductivity and ease of forming.
Frigate provides brass alloys such as 230 (85/15) and 260 (70/30), known for their high formability and corrosion resistance, also referred to as red brass and yellow brass, respectively.
Metal Stamping Production Volumes
At Frigate, we cater to various metal stamping production needs,
Ideal for up to 100,000 units, bridging prototypes and mass production, testing market viability, and accommodating customization.
Ranging from 100,000 to 1 million units, offering flexibility, lower per-part costs, and reduced up-front tooling expenses.
For orders exceeding 1 million parts, ensuring exceptional cost-effectiveness and efficient manufacturing solutions.
Designed for low volume runs with limited tool revisions, minimizing costs and ideal for less flexible projects or market entries.
Involving more intricate runs with variable factors, ensuring consistent quality, low per-unit costs, and high throughput rates for large-scale production.
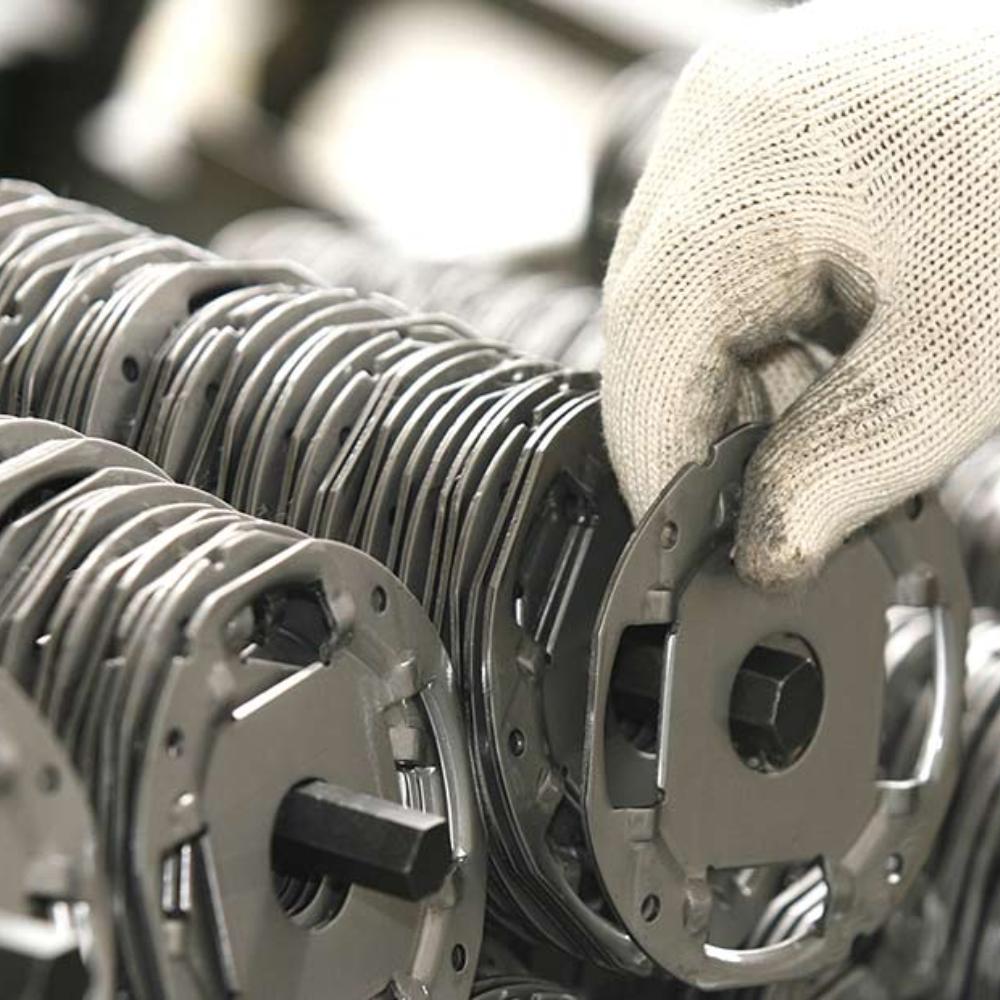

Tight Tolerances and Quality Assurance
Our suppliers refine tool and die designs to meet tolerance requirements, ensuring precise results. Tighter tolerances increase complexity and cost.
Regular checks verify output adherence to specifications, supported by a Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) program for quality and consistency. Stamping tools undergo wear detection, and measurements with check-fixtures or check-gauges are standard for long-run stamping lines. v
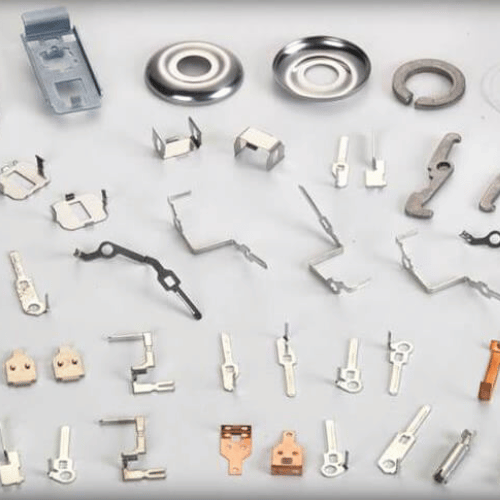

Our Stamping Process
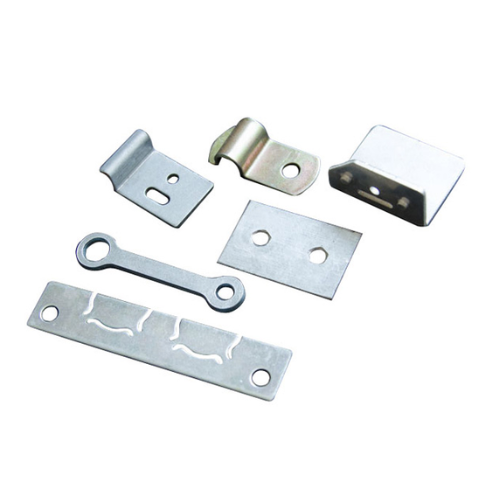






The die is engineered with advanced features such as progressive and compound tooling, ensuring efficient production for complex geometries and high-volume runs. This minimizes tool wear and maximizes throughput.
Advanced stamping relies on precise material flow control during deformation. Understanding the material's strain-hardening behavior and utilizing proper clearance in the die helps prevent tearing or wrinkling.
Using servo-driven presses allows for adjustable speed and force during stamping, optimizing cycle time and reducing part deformation variability, especially for complex parts requiring precise forming.
Material properties, such as tensile strength and yield strength, are carefully accounted for in the die design and stamping force calculation to prevent cracking and to ensure consistent part quality throughout the production run.
Advanced robotic systems and conveyors are integrated into the stamping line to automate material handling, reducing human error and ensuring smooth transitions between blanking, forming, and finishing stages.
Real-time monitoring systems track parameters like force, stroke, and material temperature during stamping. These systems allow immediate adjustments to the process, ensuring precise quality control and reducing defects.
Frigate Approach
Why Select Frigate for Stamping Metal?
With the variety of options, you can tailor your metal stamping order to your requirements. Our diverse range of materials, coatings, tolerances, and certifications guarantees that your requirements are satisfied.
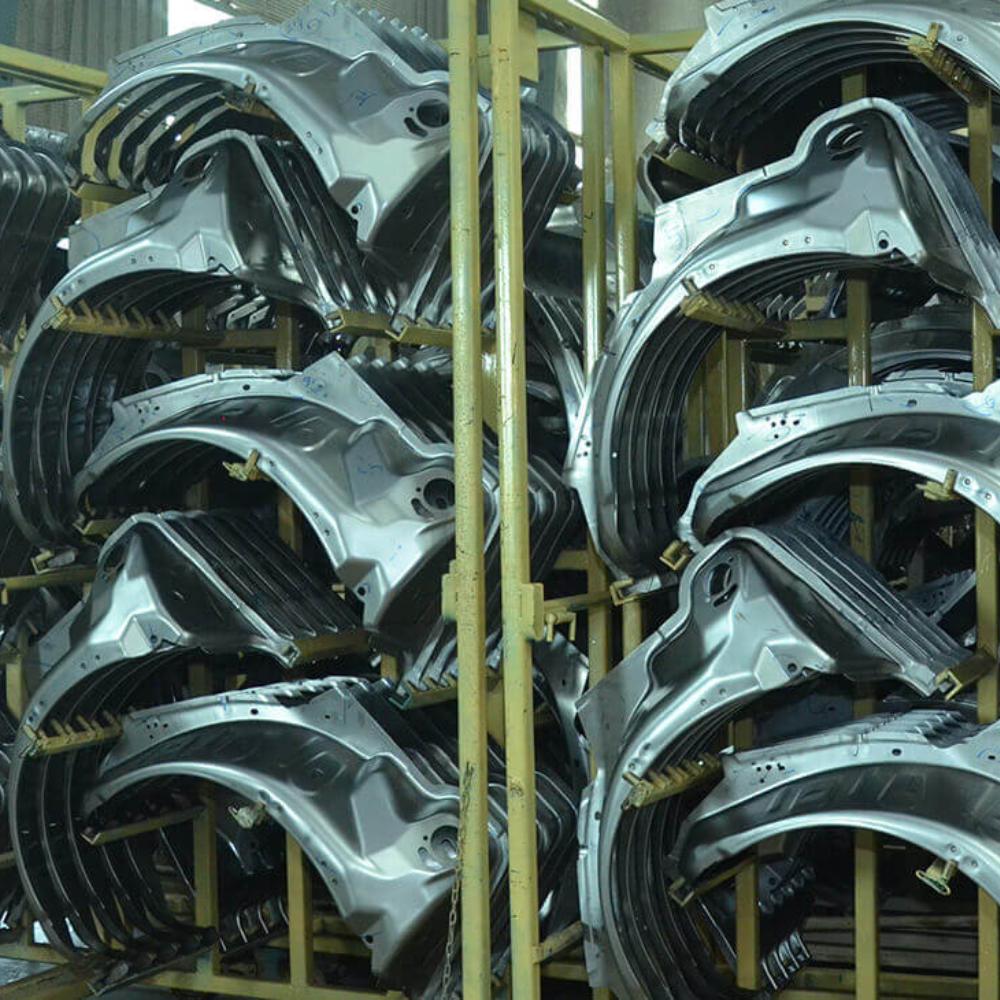

Compliance for Stamping Services
We ensure full compliance with industry standards and regulations in every stamping project. Our commitment to quality and safety is reflected in our meticulous adherence to relevant compliance protocols, which ensure both precision and reliability. We follow a robust process that integrates advanced technologies while meeting stringent performance and environmental responsibility requirements.
Key Compliance for Stamping Services
Quality management system ensuring consistent and reliable production processes.
Automotive-specific quality standards for high-precision components in the automotive industry.
Compliance with European Union regulations on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
Restriction of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
Standard for the flammability of plastic materials used in devices and appliances.
Global quality management standard for the automotive industry, ensuring production excellence and continuous improvement.
Environmental management standard for sustainable and eco-friendly production practices.

Tolerance for Stamping Services
Precision tolerance for thickness variation after stamping, based on material type and processing method.
Tolerance for drilled or punched holes, considering material stretch and die design.
Tolerance for the exact position of holes or other features relative to part edges or other features.
Deviation from an ideal flat surface, typically controlled using precision stamping tools and presses.
Deviation of a line along the length of the part, often critical for structural integrity in aerospace or automotive parts.
Tolerance for any burrs formed at the edges after the stamping process, which are removed in finishing.
Tolerance for the smoothness and size of radii at the part’s edges, critical for parts that fit into assemblies.
Deviation from a right angle between two surfaces or features of the stamped part.
Dimensional accuracy for overall part size, crucial for ensuring parts fit into larger assemblies.
Tolerance for the depth of formed sections, depending on the material and stamping technique used.
Tolerance for the bow or curve in a flat part after stamping, affecting assembly accuracy.
Surface roughness values after stamping, significant for parts that require aesthetic or functional smoothness.
The degree to which multiple holes or features align to a central axis. Essential in precision assemblies.
Tolerance for the radius at corners, important for both aesthetic and structural integrity.
Variation in material thickness across the entire part, ensuring uniform strength and consistency.
Tolerance for angular deviation due to the elasticity of the material after forming.
Variation in the material’s tensile strength after stamping, affecting the part’s durability and load-bearing ability.
Tolerance for hardness across the stamped part, crucial for components requiring specific strength or wear resistance.
Tolerance for thread dimensions on stamped parts, especially in fasteners or mechanical components.

Quality Testing Standards for Stamping Services
Tests the material's ability to withstand forming without failure, determining the limits of deformation.
Detects any deformation or distortion in hole geometry caused by the stamping process.
Determines the force required to shear the material, ensuring the integrity of edges and joints.
Measures the minimum bend radius that can be achieved without causing cracking or material failure.
Measures the increase in hardness and strength of the material during the deformation process.
Tests the angular deformation that occurs after material release from tooling, to ensure part accuracy.
Evaluates the material's ability to withstand repeated stress and strain, ensuring durability in applications with dynamic loads.
Measures the height of flanges post-stamping to ensure consistent feature dimensions.
Ensures the stamped features are aligned precisely according to the part design.
Assesses the resistance to sliding between stamped parts or materials, which is critical for part function.
Measures the size and shape of burrs left on the stamped part, ensuring they are within acceptable limits for assembly.
Measures the uniformity and thickness of coatings applied post-stamping for corrosion protection.
Evaluates the part’s ability to maintain its properties under high-temperature conditions.
Examines the grain structure of the material after stamping to ensure no detrimental changes in microstructure.
Measures internal stress that may be induced during stamping, ensuring it does not affect part performance.
Measures the frictional properties between the stamped part and contacting surfaces during operation.
Analyzes the amount of material strain during stamping to predict and prevent failure or cracking.
Detects any warping or twisting in the part after stamping, ensuring it fits properly in assemblies.
Assesses how well the stamping die fills, ensuring the material flows consistently and evenly throughout the die.
- Real Impact
Words from Clients
See how global OEMs and sourcing heads describe their experience with our scalable execution.
“Quick turnaround and solid quality.”
“The instant quote tool saved us time, and the parts were spot-on. Highly recommend Frigate!”
“I would strongly recommend Frigate to anyone who wants to do Rapid Prototyping, and take their ideas to manufacturing. One firm doing all kinds of Product Development!”
“Great service, fair price, and the parts worked perfectly in our assembly.”
“Top-notch machining and fast shipping. Very satisfied with the results.”
“The next disruption is happening in Prototyping & Manufacturing on-demand and Frigate is leading the way! I personally believe the Frigate's way of IIOT enabled cloud platform with Al.”
“Frigate delivered high-quality parts at a competitive price. The instant quote tool is a huge plus for us!”
“We appreciate the precision and quality of the machined components in the recent delivery—they meet our specifications perfectly and demonstrate Frigate’s capability for excellent workmanship.”
“Flawless execution from quote to delivery.”
“I am absolutely happy to work with supplier like Frigate who were quite proactive & result oriented . Frigate has high willingness team who has strong know how & their passion towards the products & process were absolutely thrilling.”
“The precision on these parts is impressive, and they arrived ahead of schedule. Frigate’s process really stands out!”
“Parts were exactly as spec’d, and the instant quote made budgeting a breeze.”
“Good value for the money.”
“The finish was perfect, and the team was easy to work with.”
“Working with Frigate has been great. Their proactive, results-driven approach and expertise shine through in every project. It's been a pleasure collaborating with them.”
"We are highly satisfied with the timely delivery and quality of the MIG Welding Cable from Frigate. Their attention to detail, secure packaging, and quick responsiveness stood out. We confidently recommend Frigate Engineering Services Pvt. Ltd. as a reliable manufacturing partner."
Having Doubts? Our FAQ
Check all our Frequently Asked Question
It's a metal-forming technique utilized to craft intricate parts for diverse industries, consolidating multiple processing steps into a single operation. The benefits include enhanced speed and precision in production.
Numerous industries, including the automotive, manufacturing, construction, aerospace, electronics, medical, and more, use metal stampings.
It is a cost-effective method of creating a variety of components in a range of sizes, shapes, levels of complexity, and accuracy. The fact that deep-drawn car parts are manufactured with a complete wall surrounding the full diameter without any seams is one of its main advantages.
While fine blanking suppresses the ripping of sheet metal material during the blanking process, general stamping regulates the tearing of the material during the blanking process
Frigate's industry expertise and AI-enabled platform, which can analyze design complexity, will assist you in selecting the best course of action.
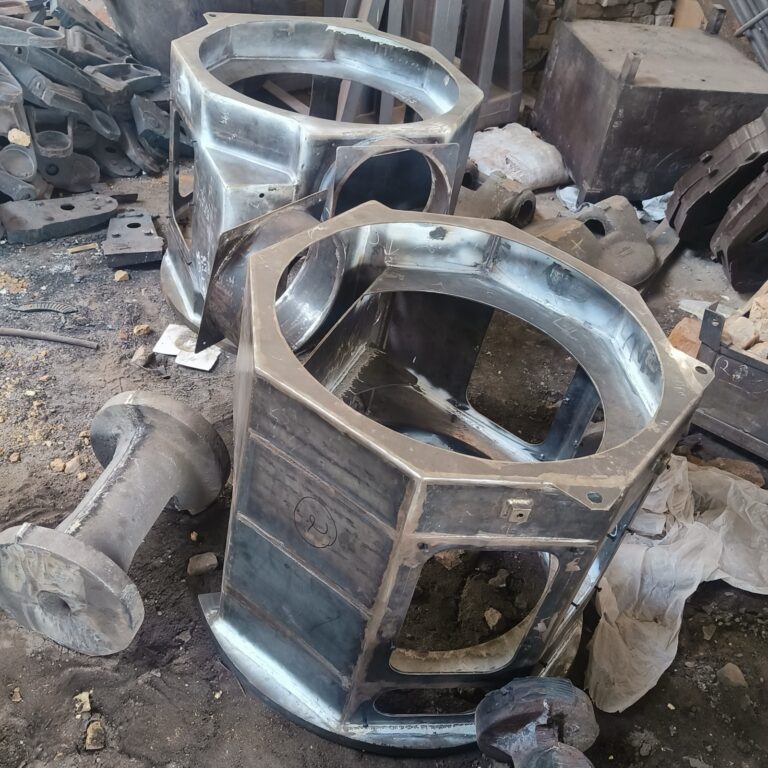
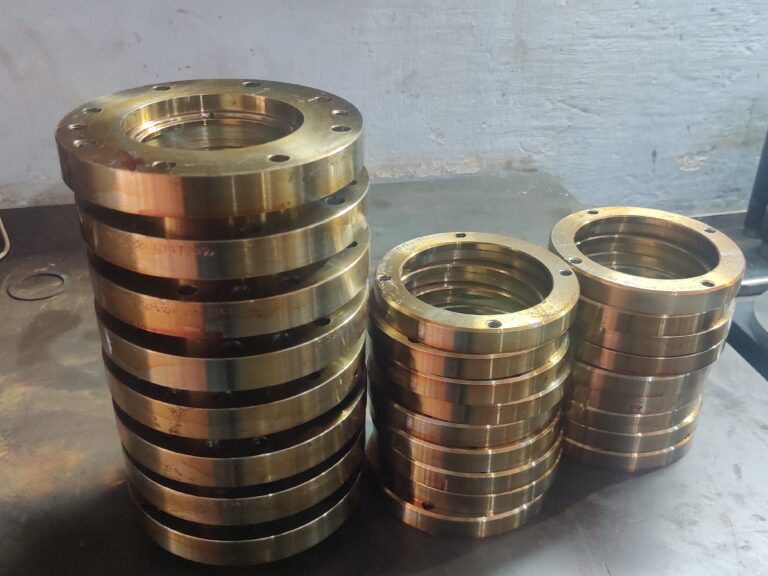
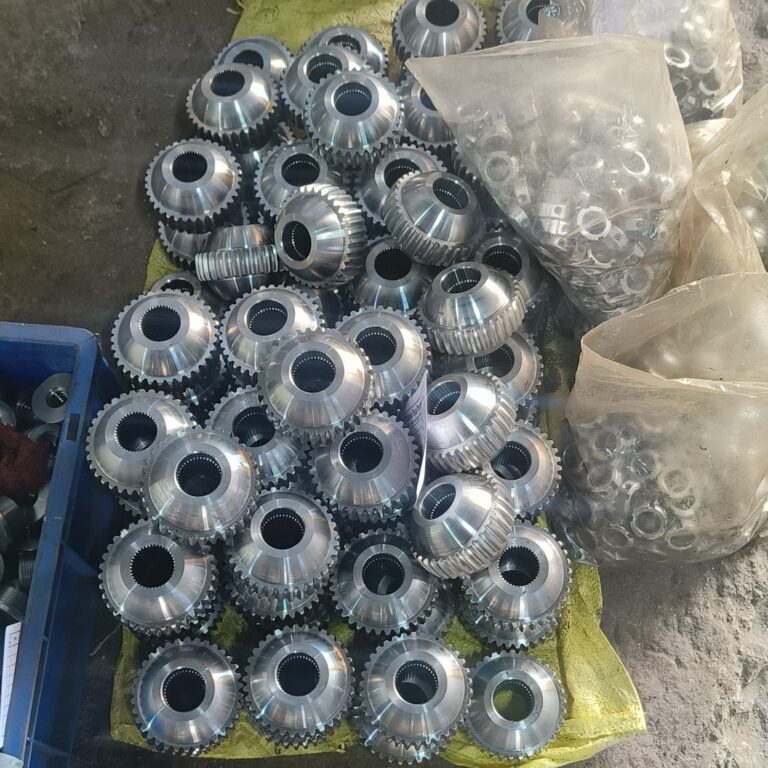
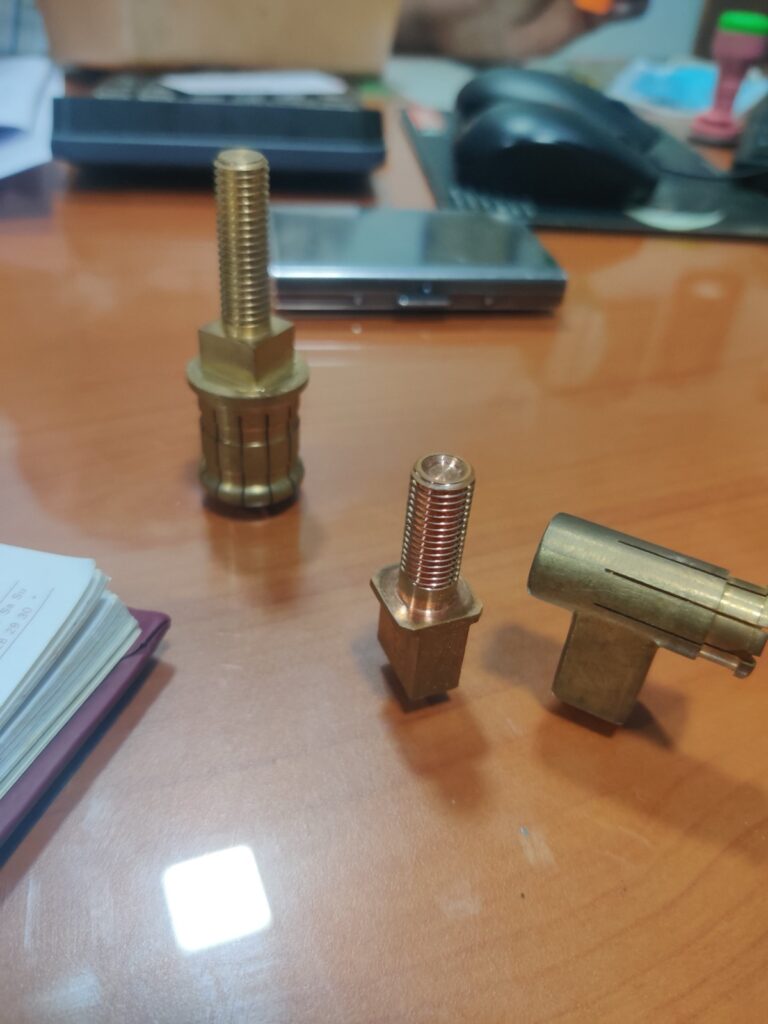
Manufacturing Capability/Capacity
Ferrous casting
Mold size(max): 1m X 1m
Weight Range: 1 KG ~ 30 KGS
Mold size(max): 1.5m X 1.5m
Weight Range: 30 KG ~ 150 KGS
Mold size(max): 3m X 3m
Weight Range: 100 KG ~ 1000 KGS
Mold size(max): 500 MM X 500 MM
Weight Range: 0.250 KG ~ 20 KGS
Mold size(max): 500 MM X 500 MM
Weight Range: 0.100 KG X 20 KGS
Non-ferrous casting
Capacity: 5000 MT/a
Range of weight: 100 gm to 20 KGS
Mold size(max): 1 M X 1 M
Weight Range: 0.5 KG X 50 KGS
Mold size(max): 1 M X 1 M
Weight Range: 0.5 KG X 50 KGS
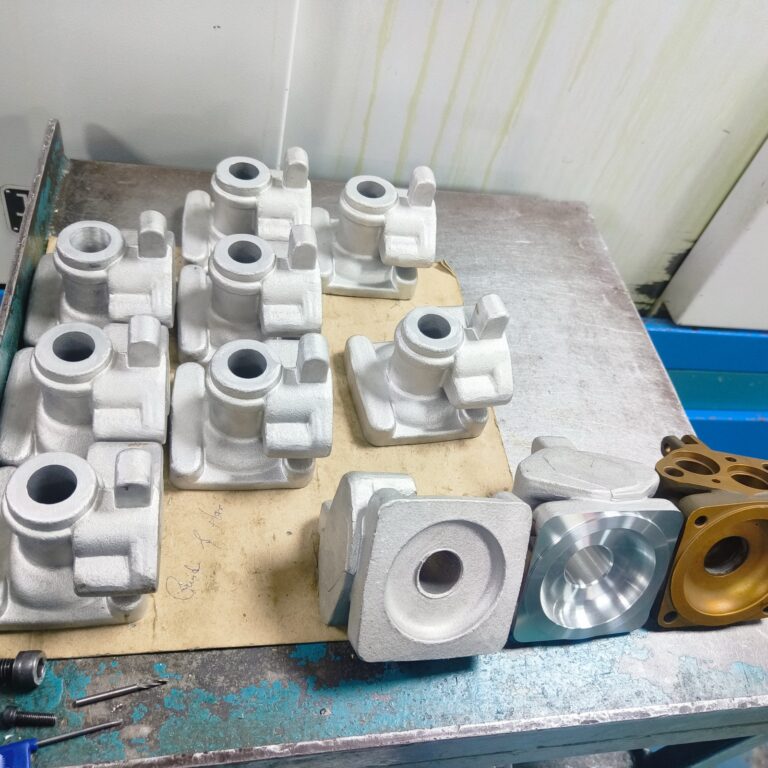
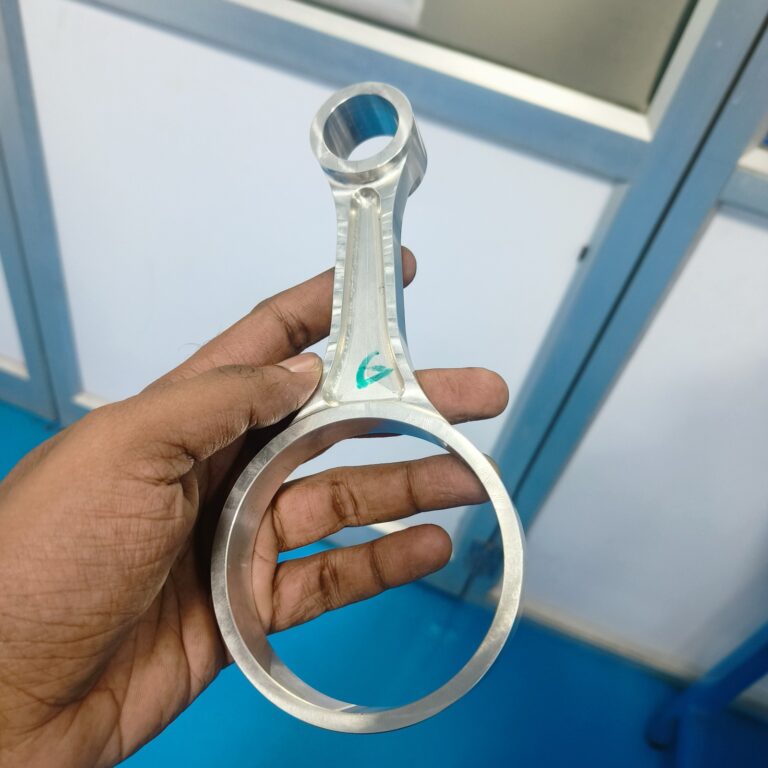
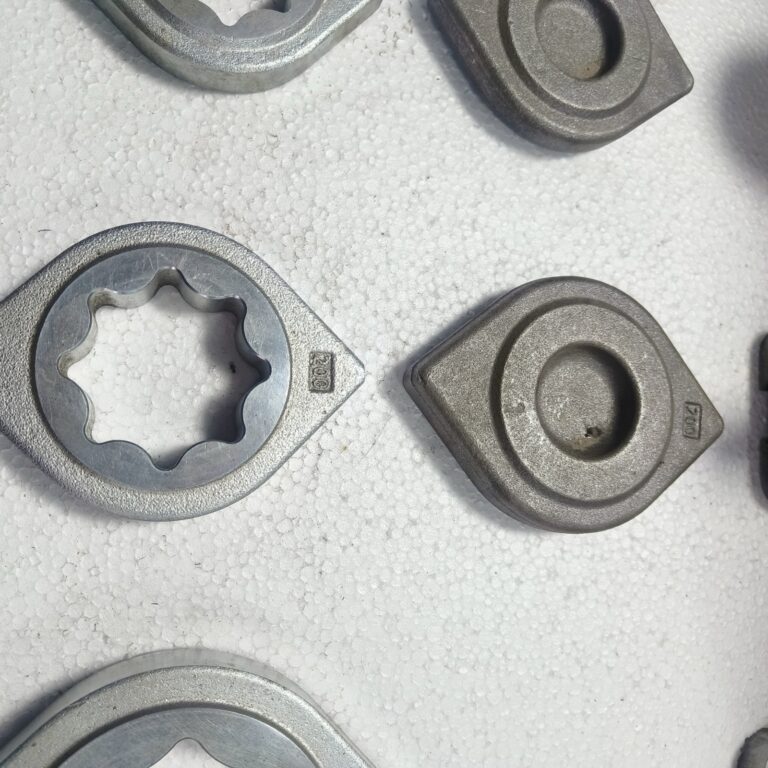
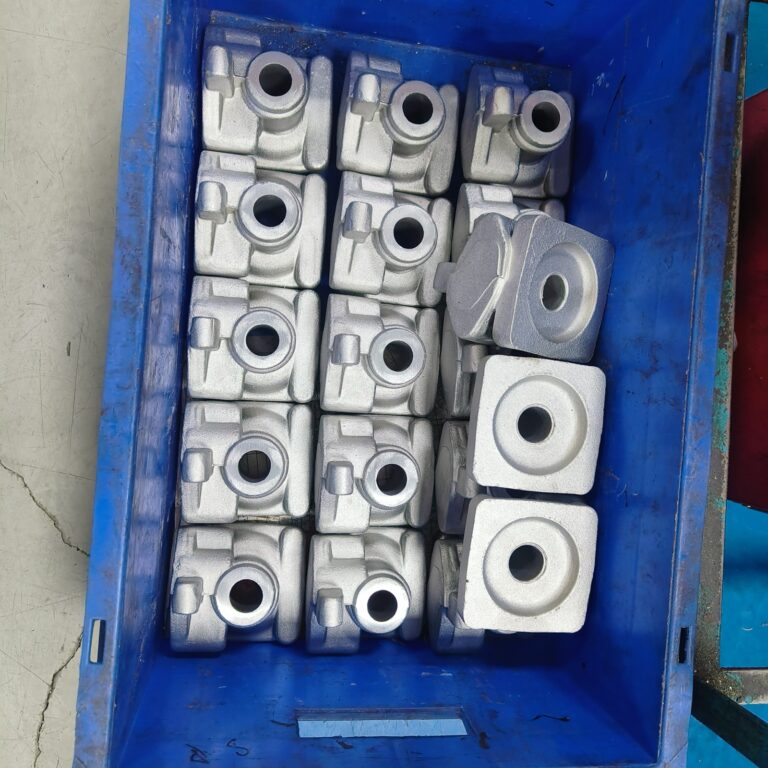
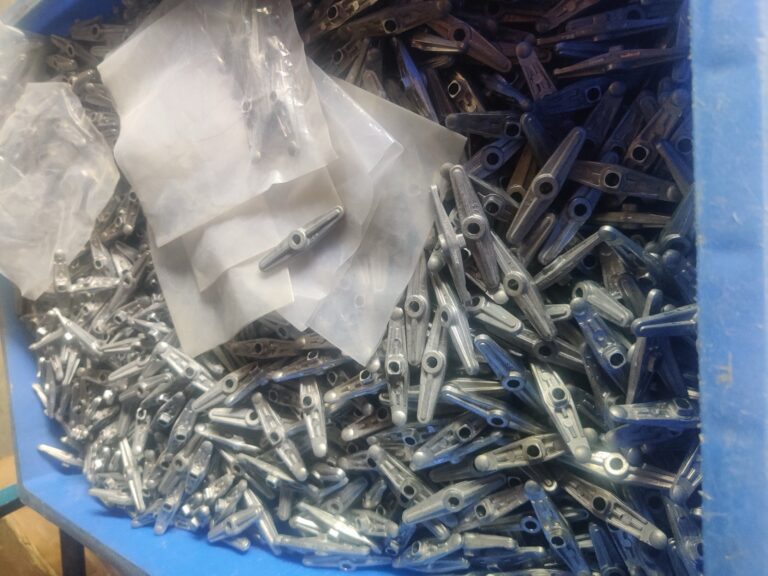
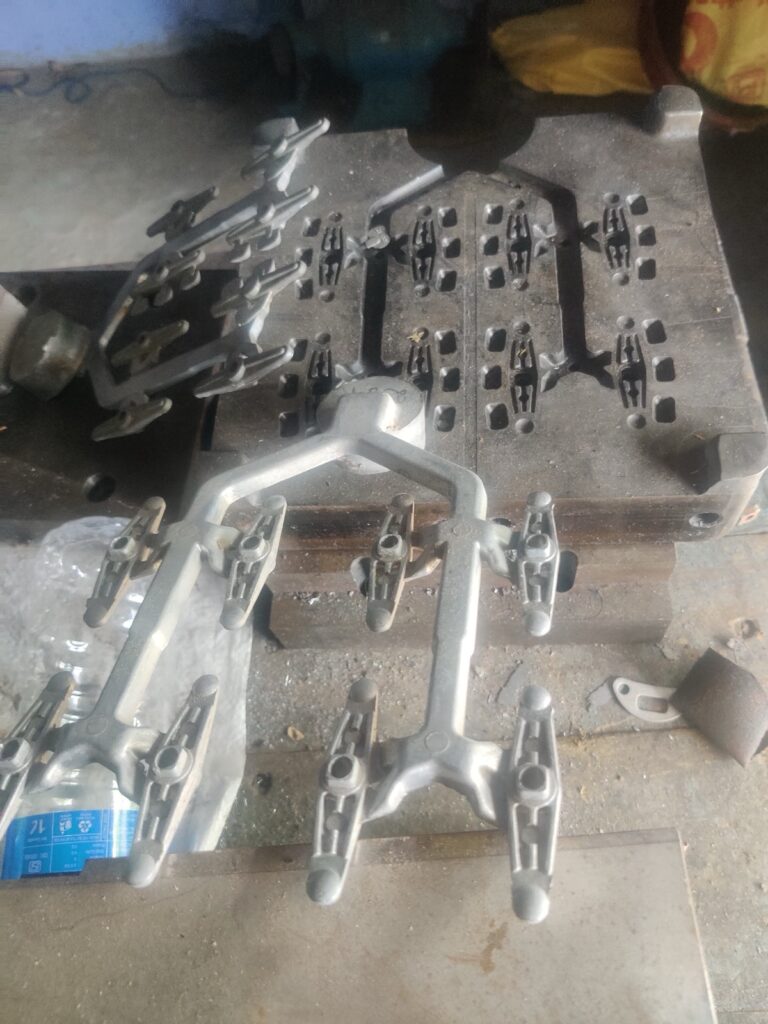










Forging
Capacity: 20,000 Tons per Annum
Range of weight: 300 KG to 1 Ton
Hammering: 5 Ton
Range of weight: 0.2 KG to 200 KGS
Hammering: 1600 Ton Hydraulic press
Ring size: 350 MM OD to 3000 MM OD
Range of weight: 15 KGS to 3200 KGS
Materials
Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel (AUSTENITE), Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel (MARTENSITE), etc.
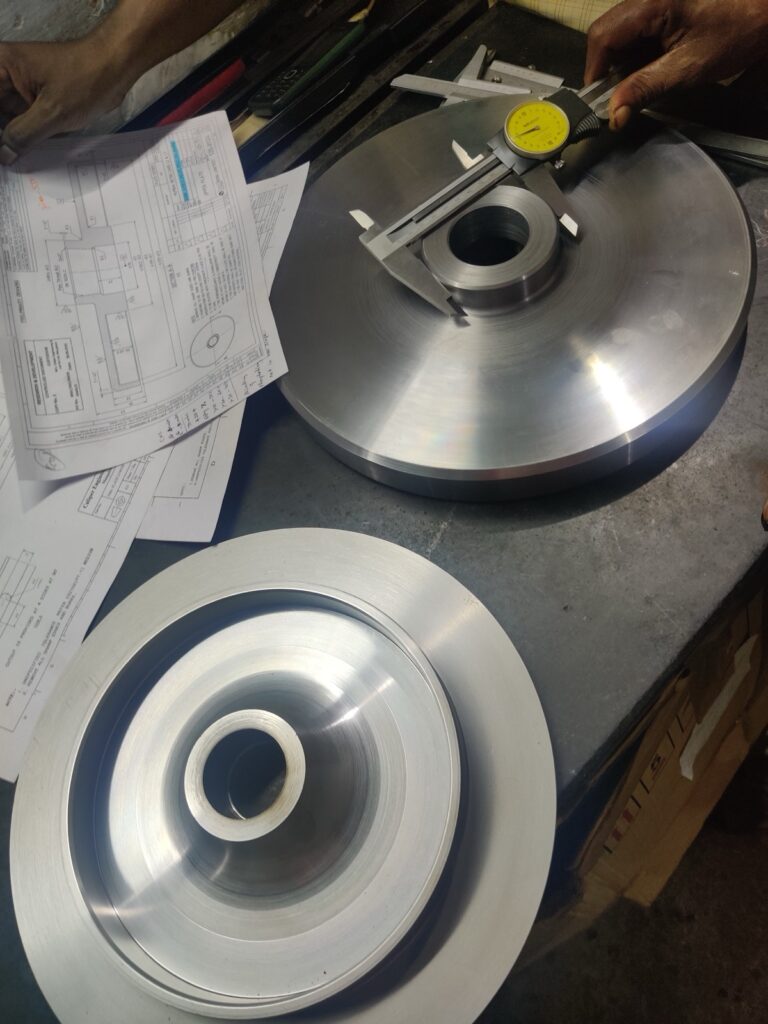
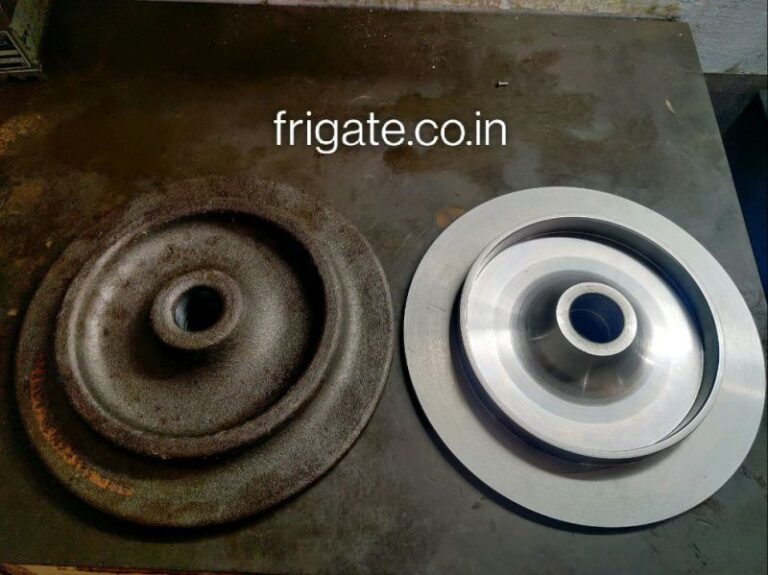
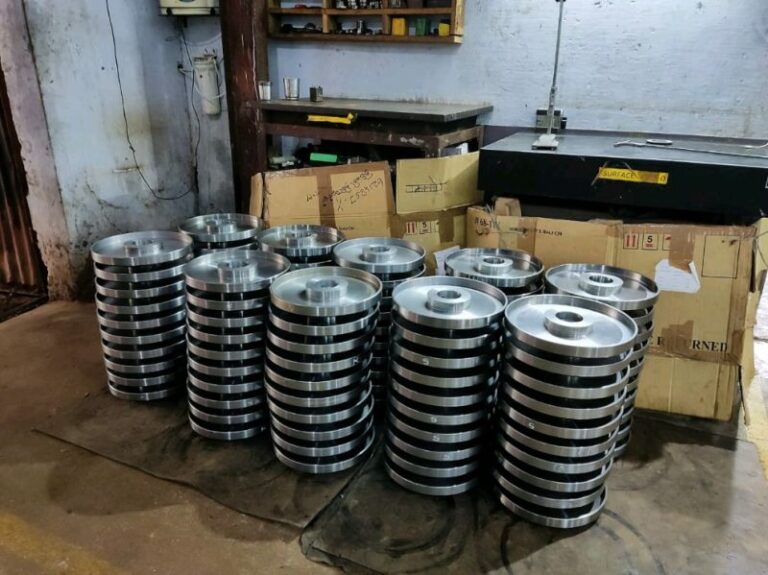
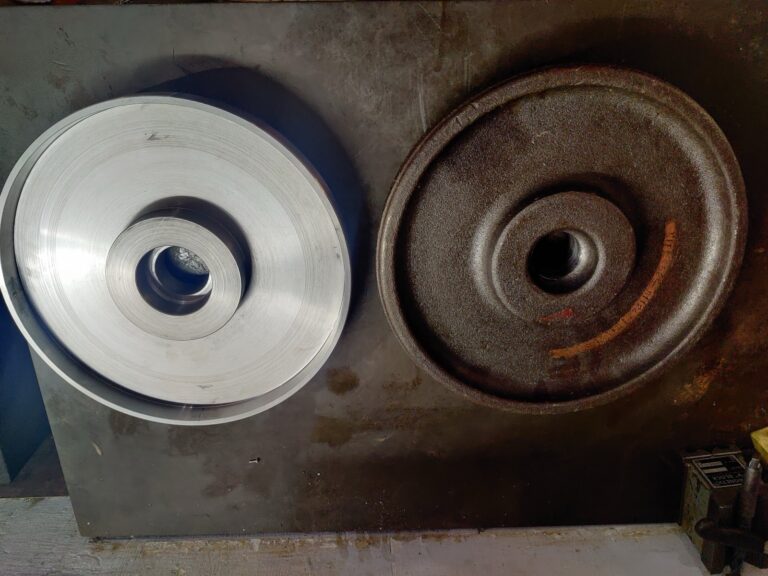





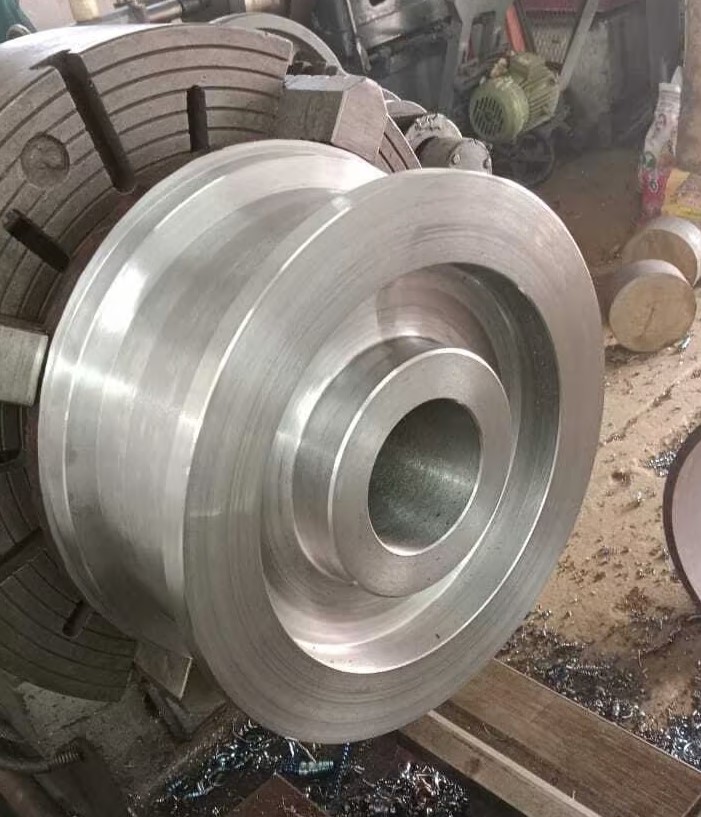
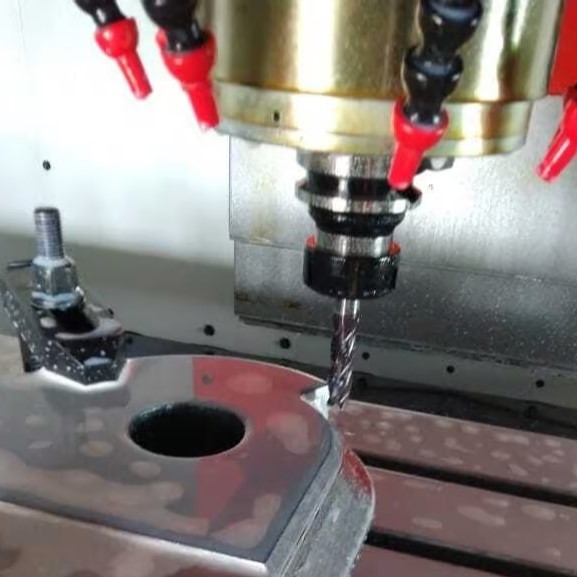
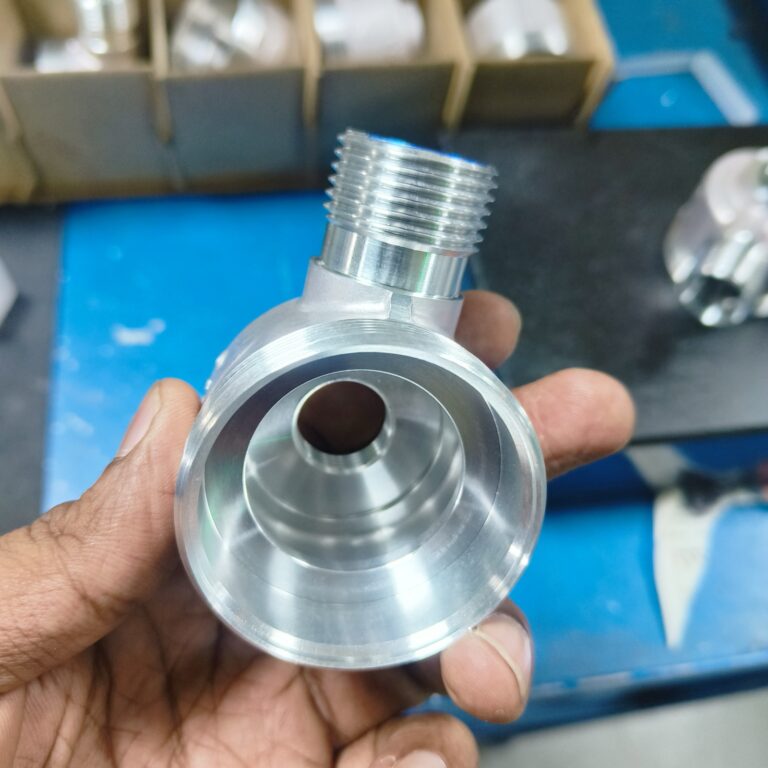
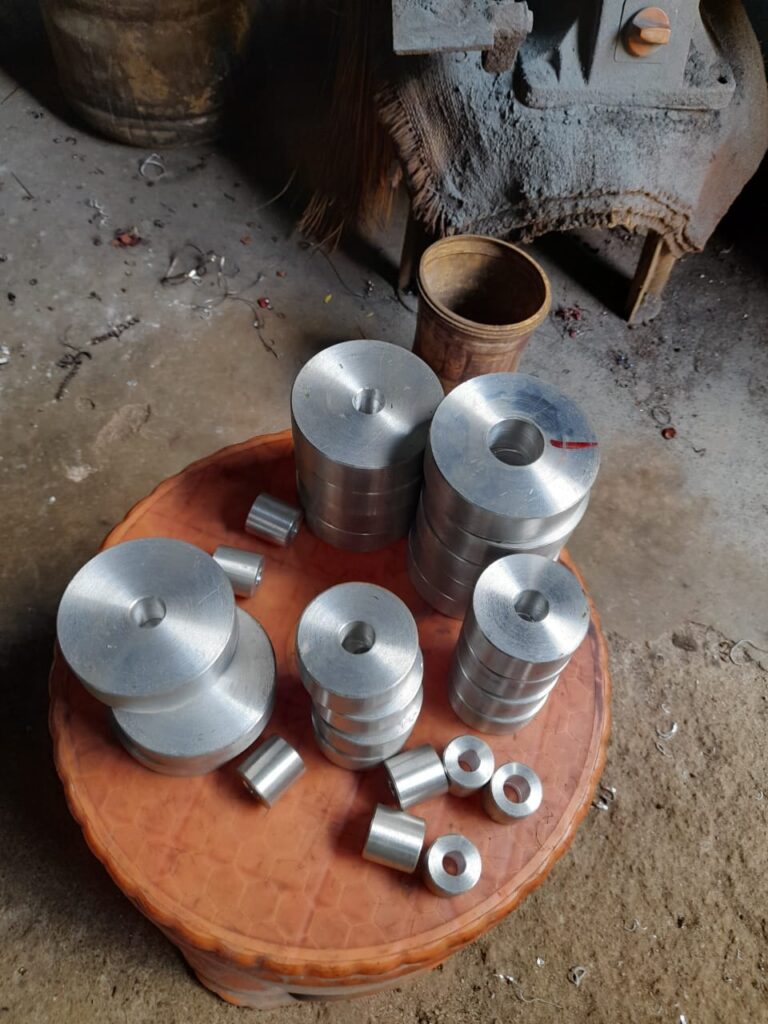
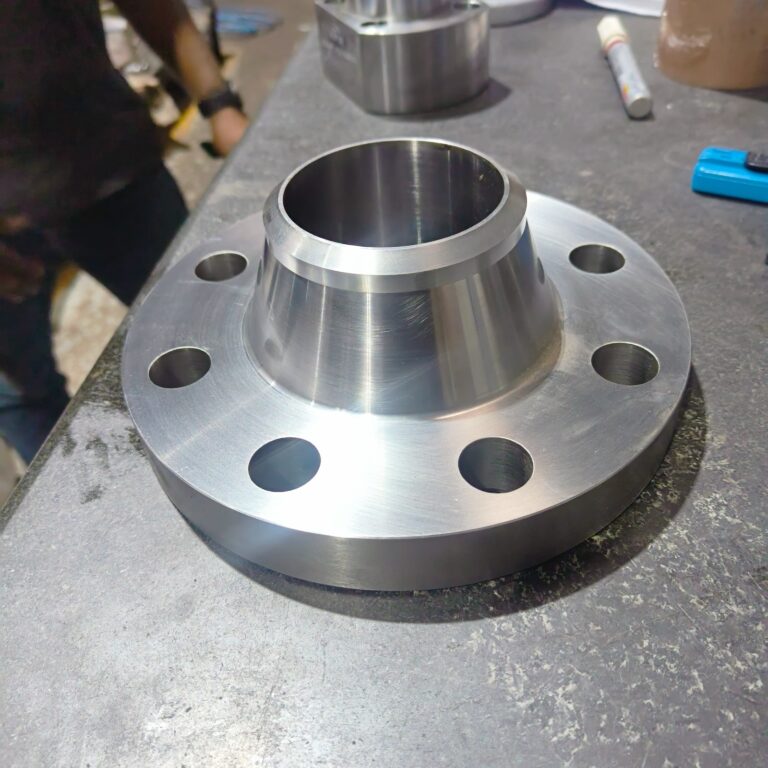
Machining
1 to 1000 MM
1 to 1000 MM
1 to 1000 MM
Materials
Steel, Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Titanium, Nickel Alloys, Tungsten Carbide, etc.
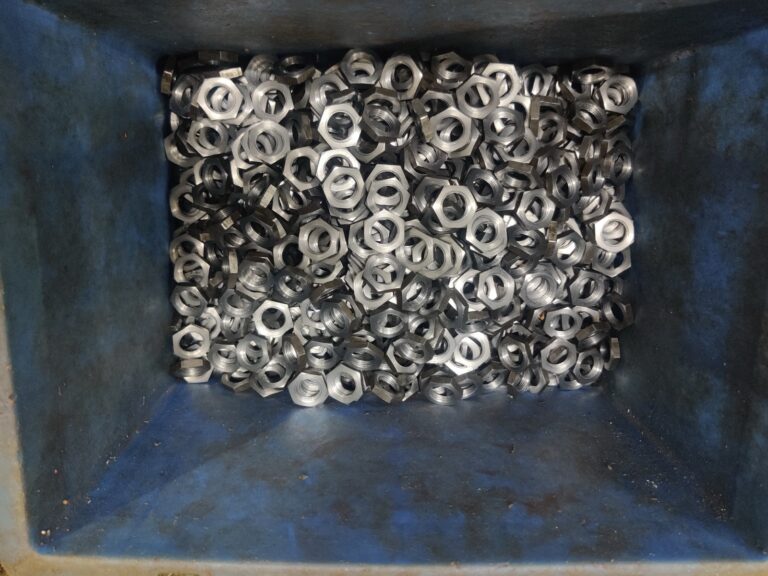
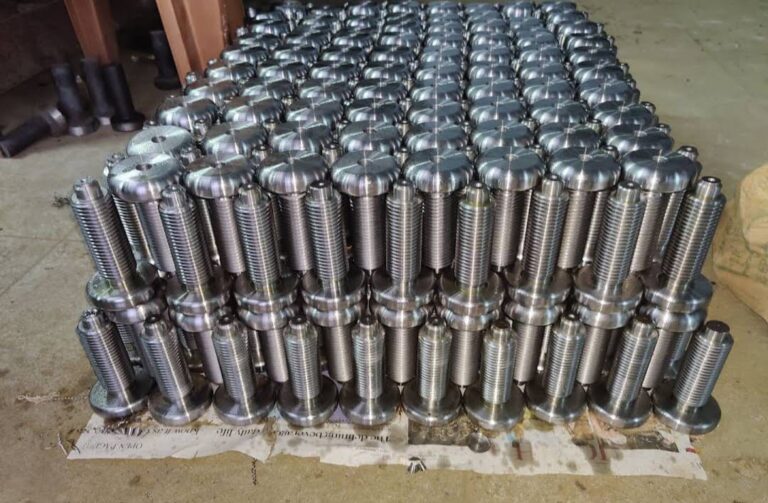
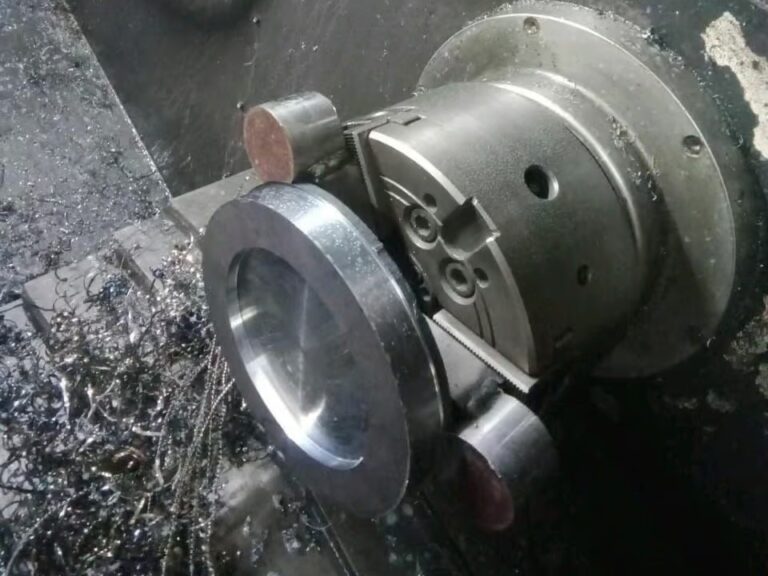
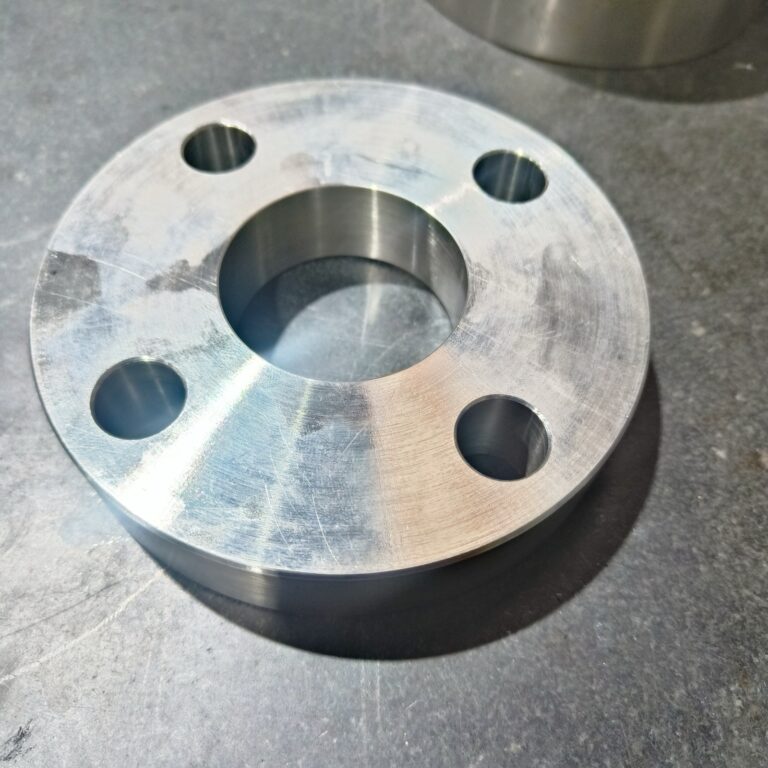
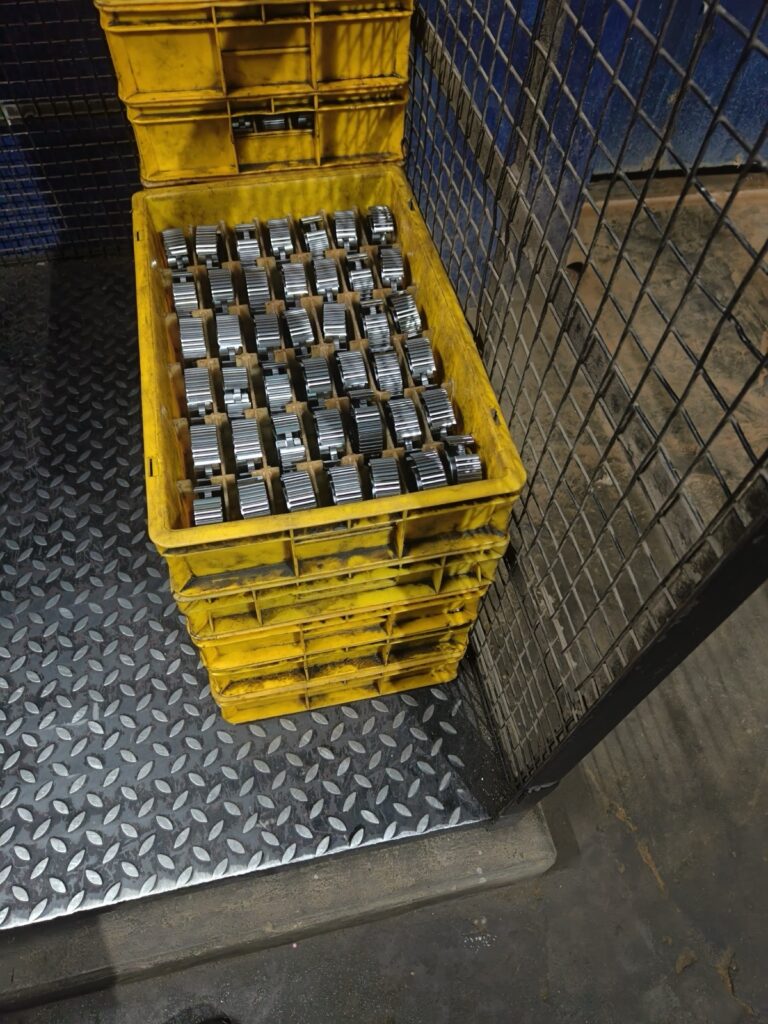
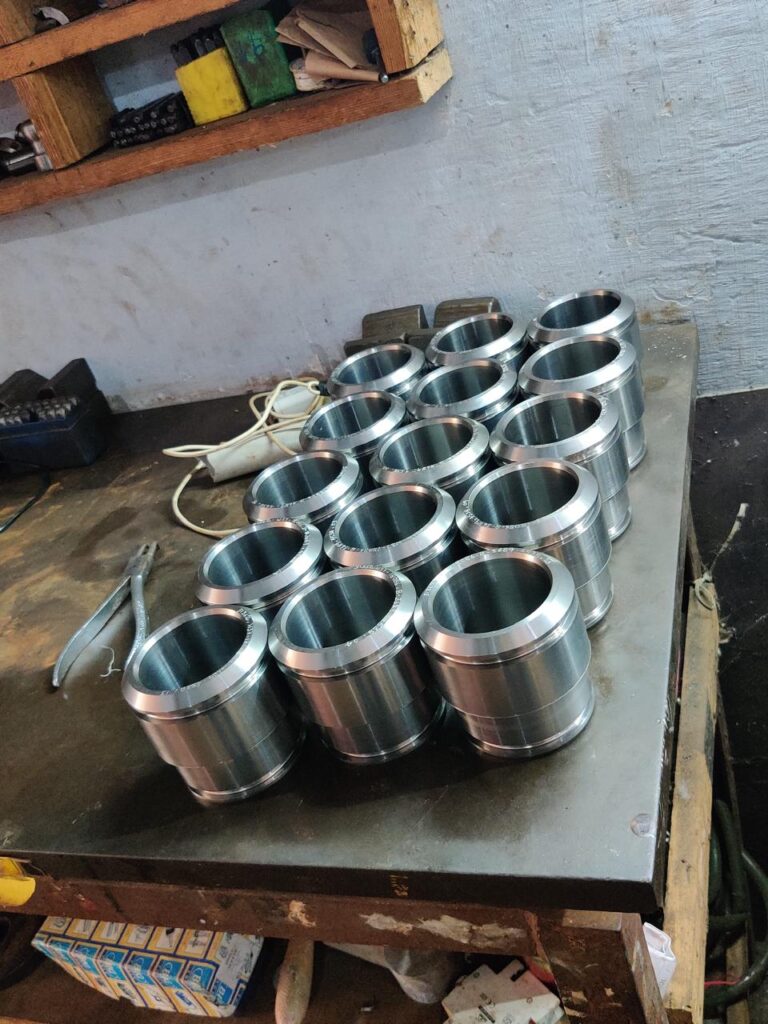
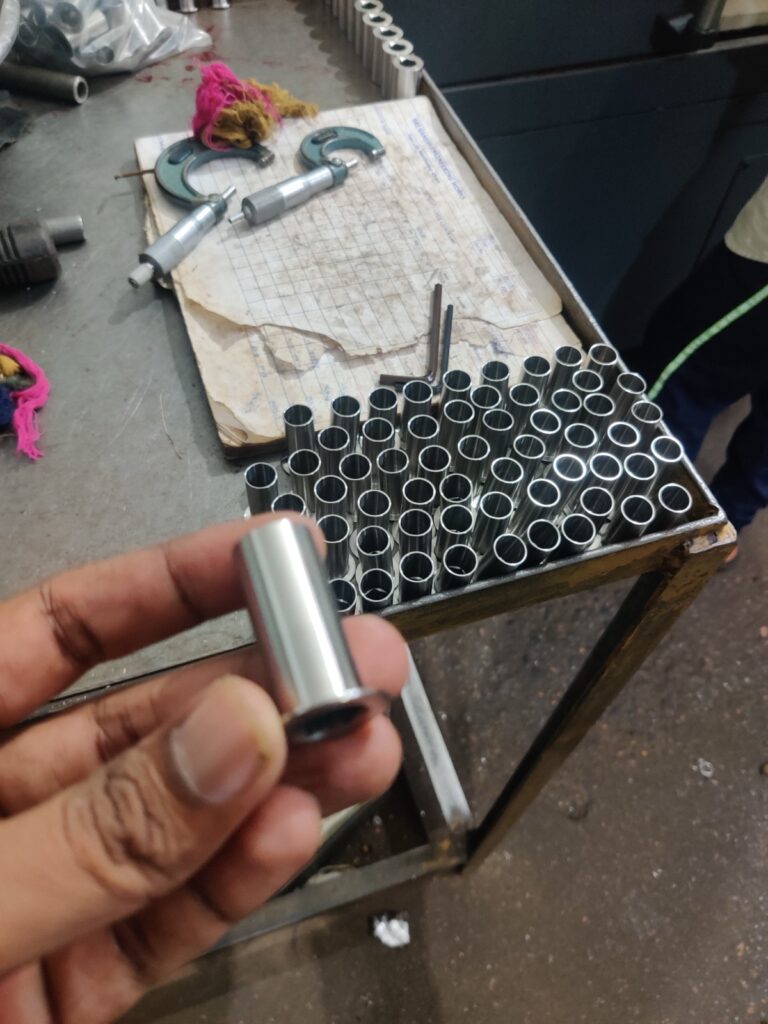
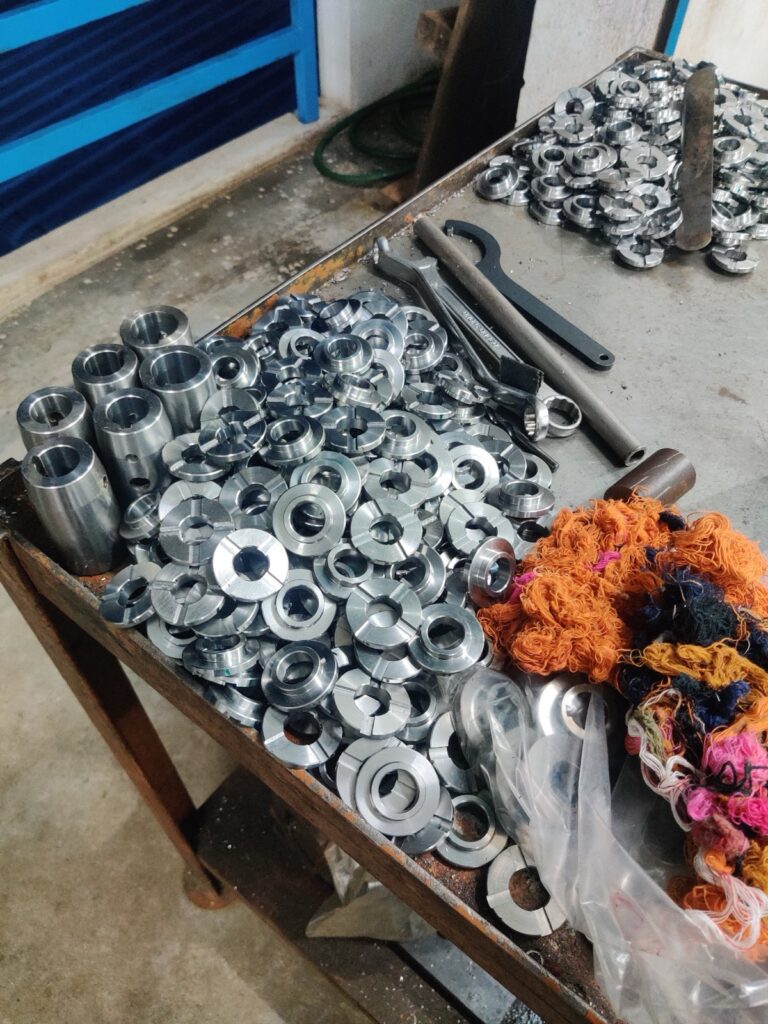
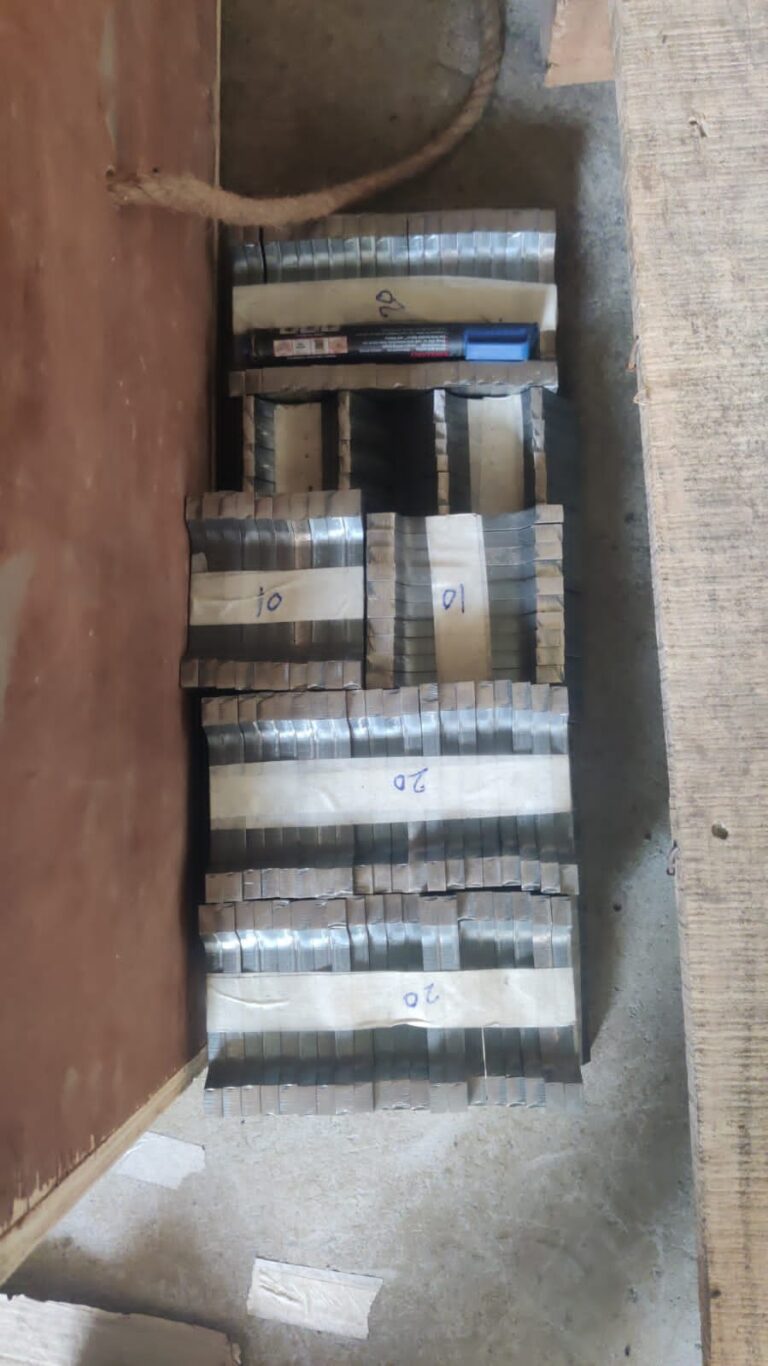
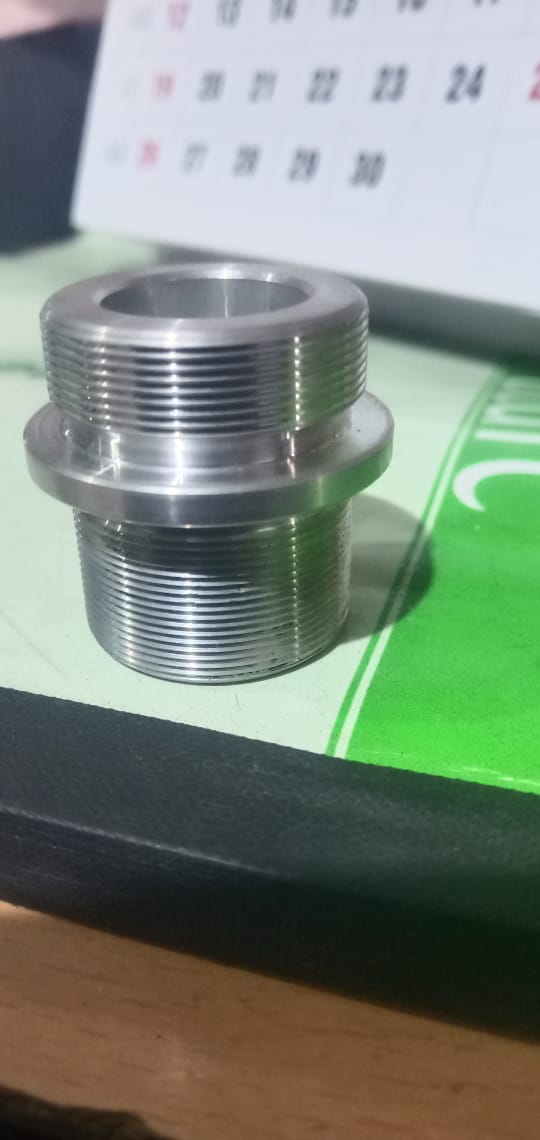
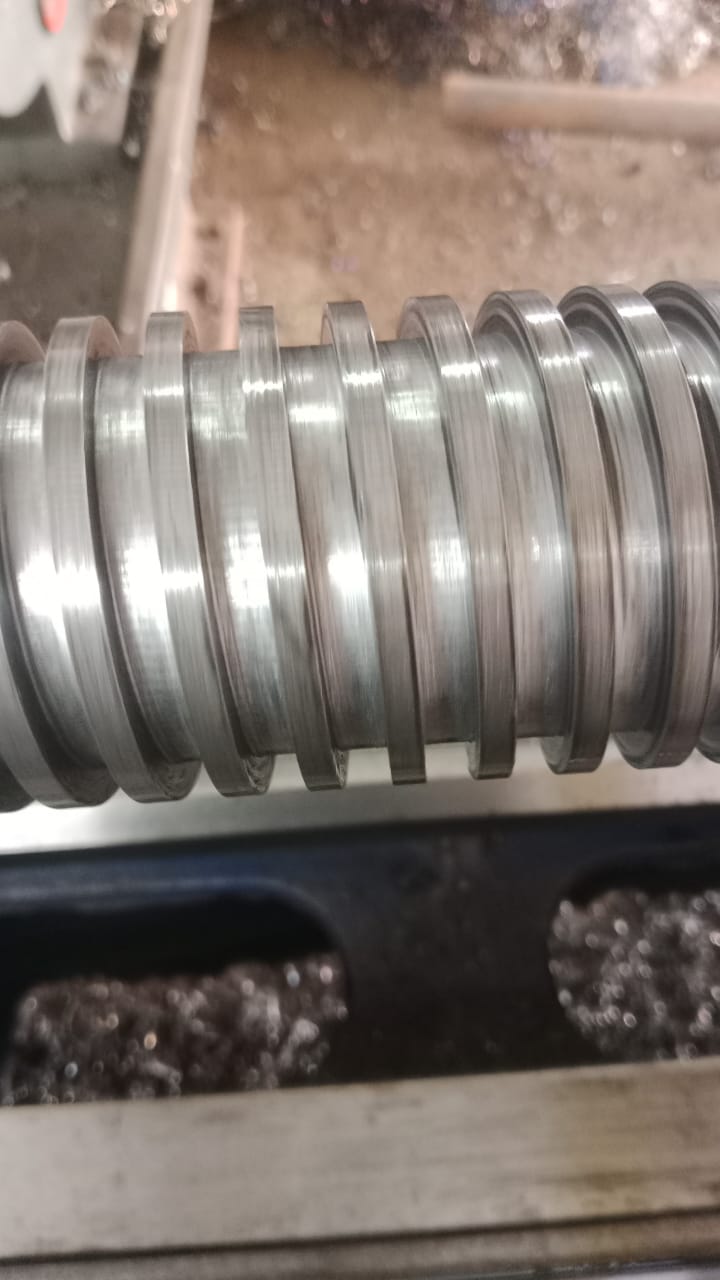
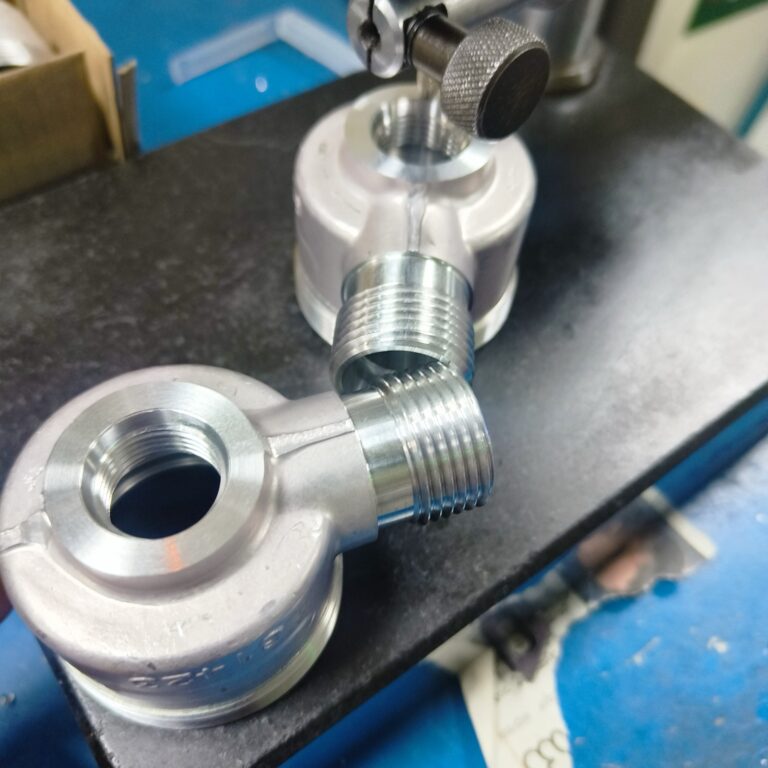


























Plastics
Materials
1250 X 1250 MM
Within 10 microns
Engineering Plastics, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polyvinyl chloride, Polyethylene terephthalate, Bioplastics, etc.
Rubber
Materials
Natural rubber, Styrene-Butadiene Rubber, Nitrile Butadiene Rubber, Silicone Rubber, Fluorocarbon Rubber, Recycled Rubber, etc.
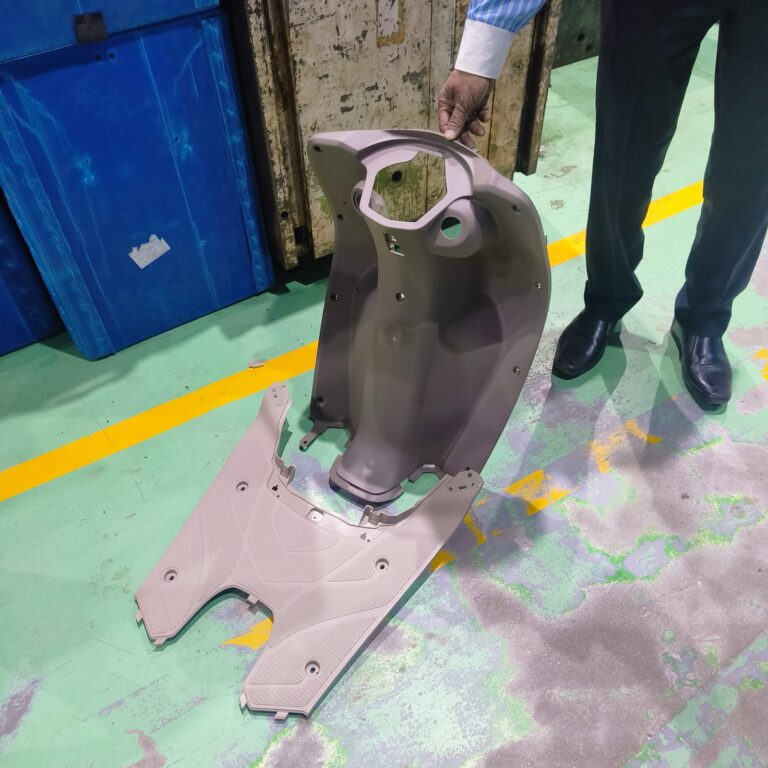
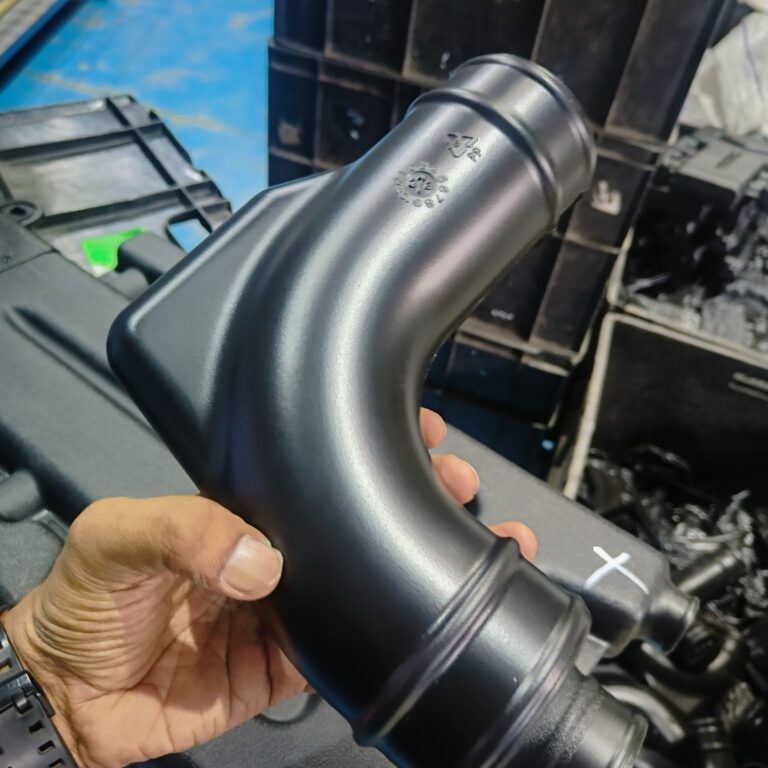
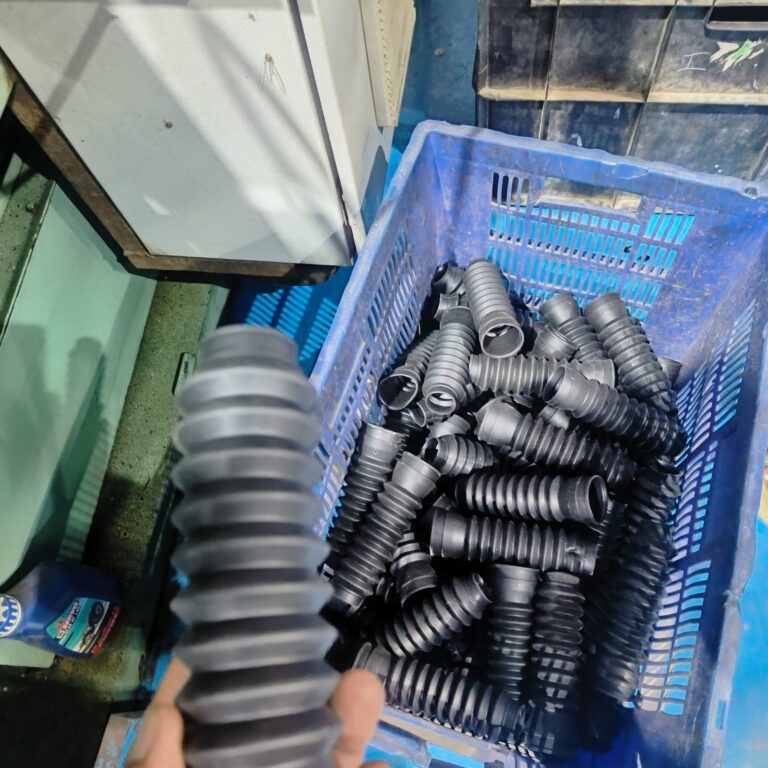
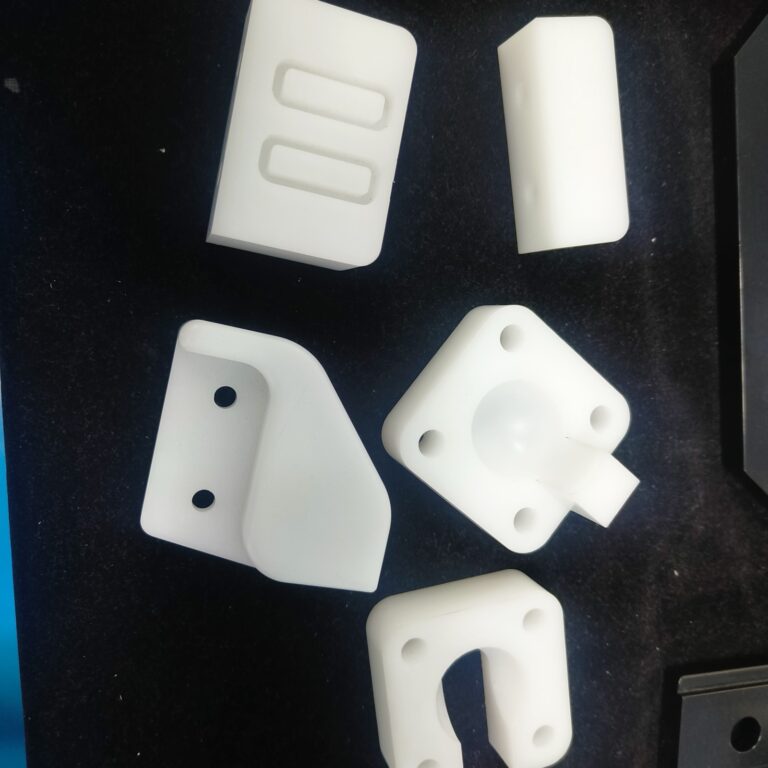
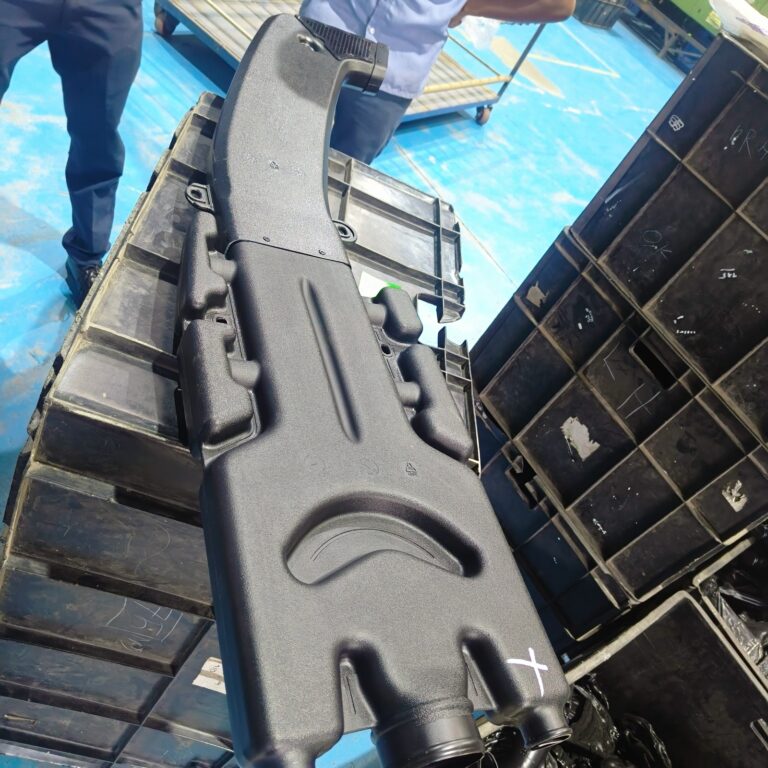
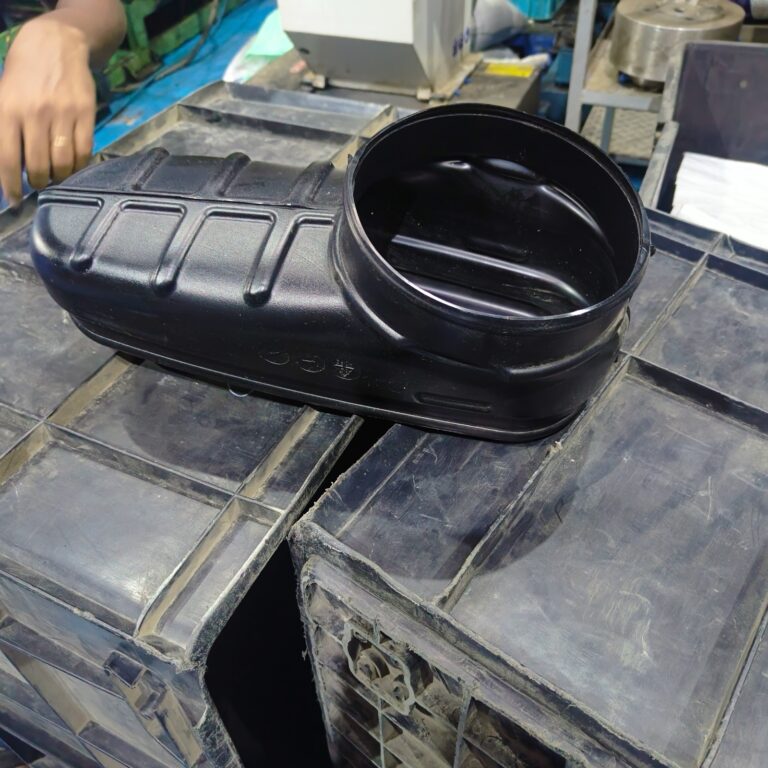
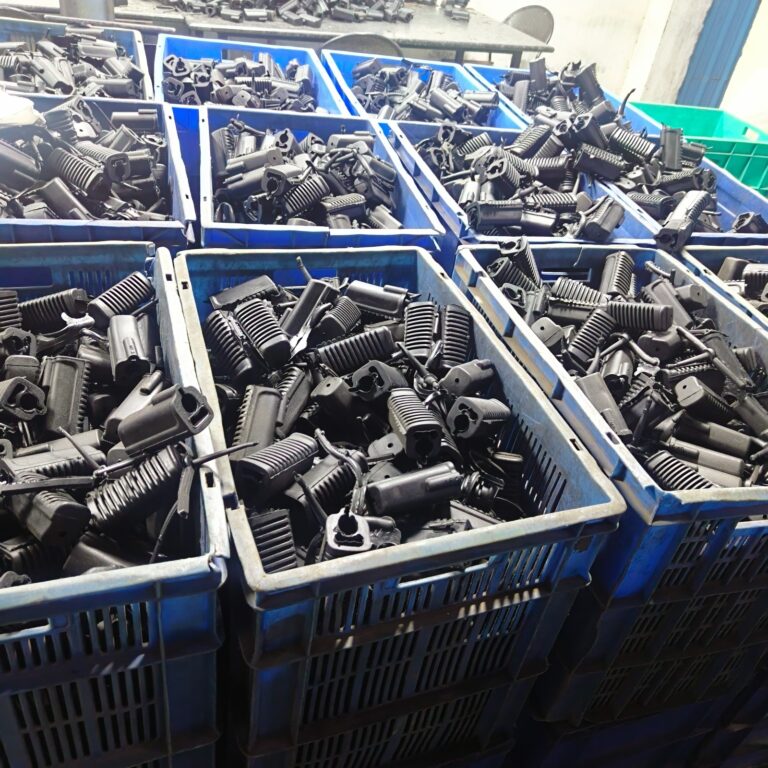
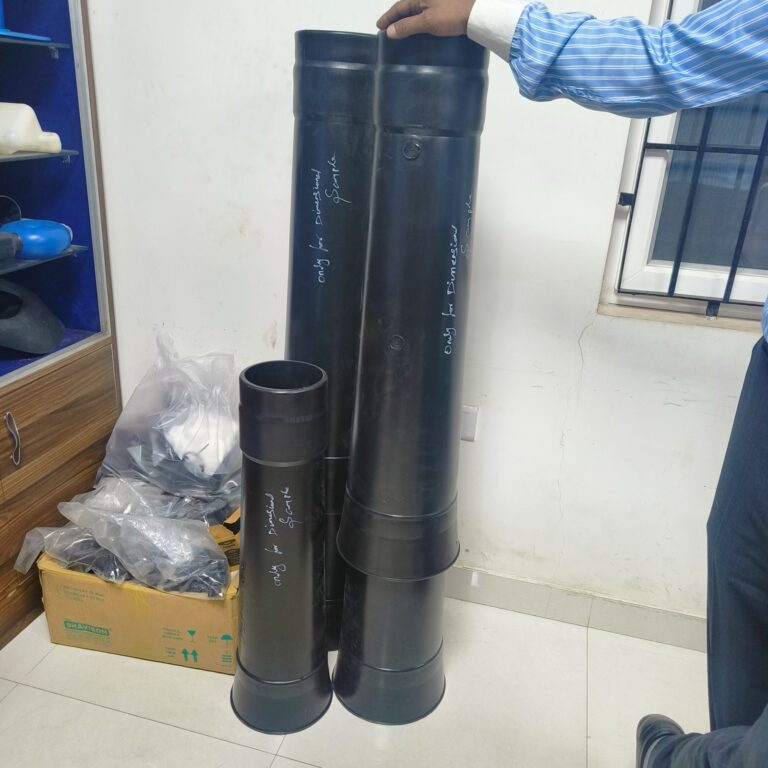
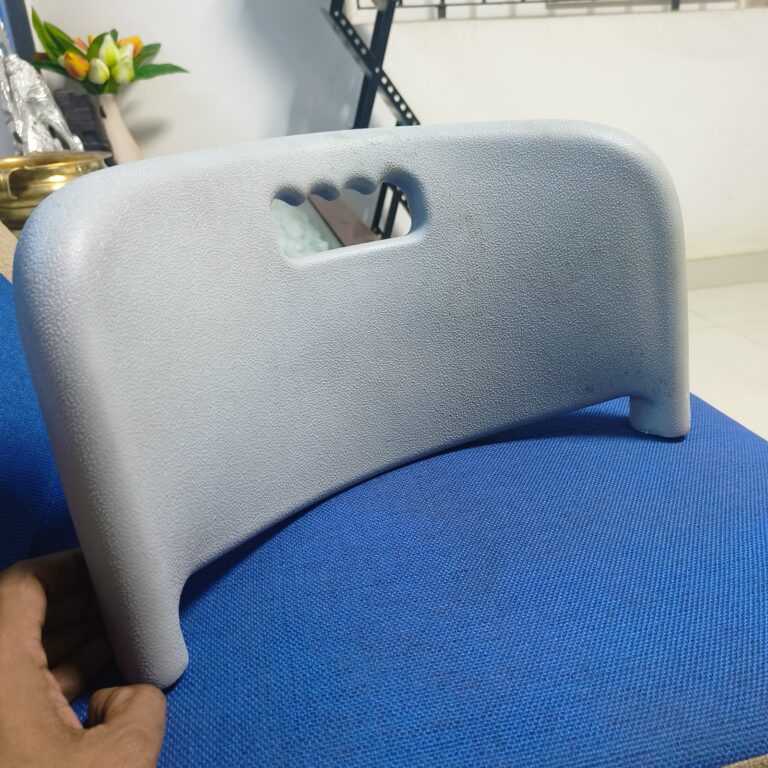
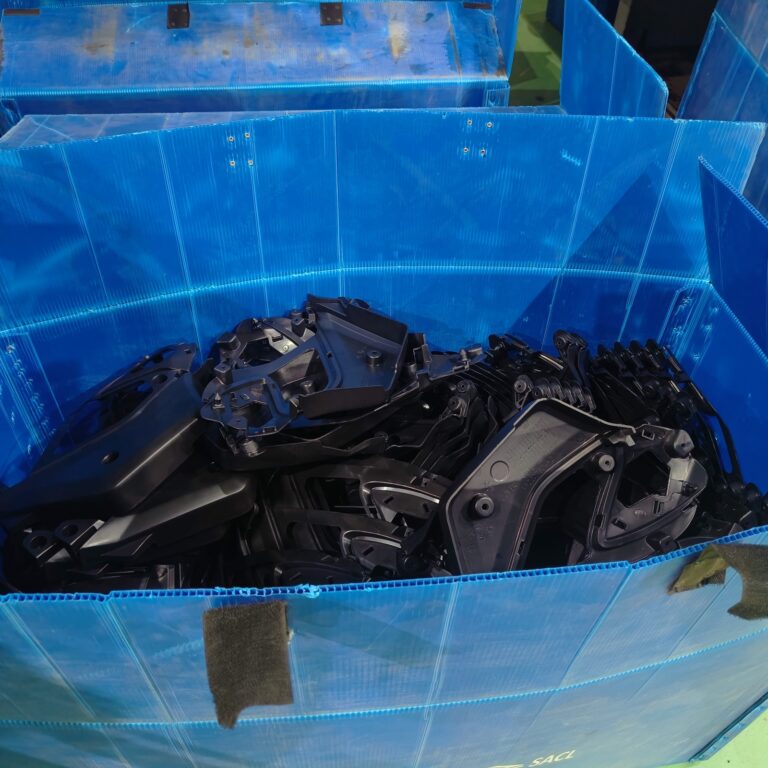
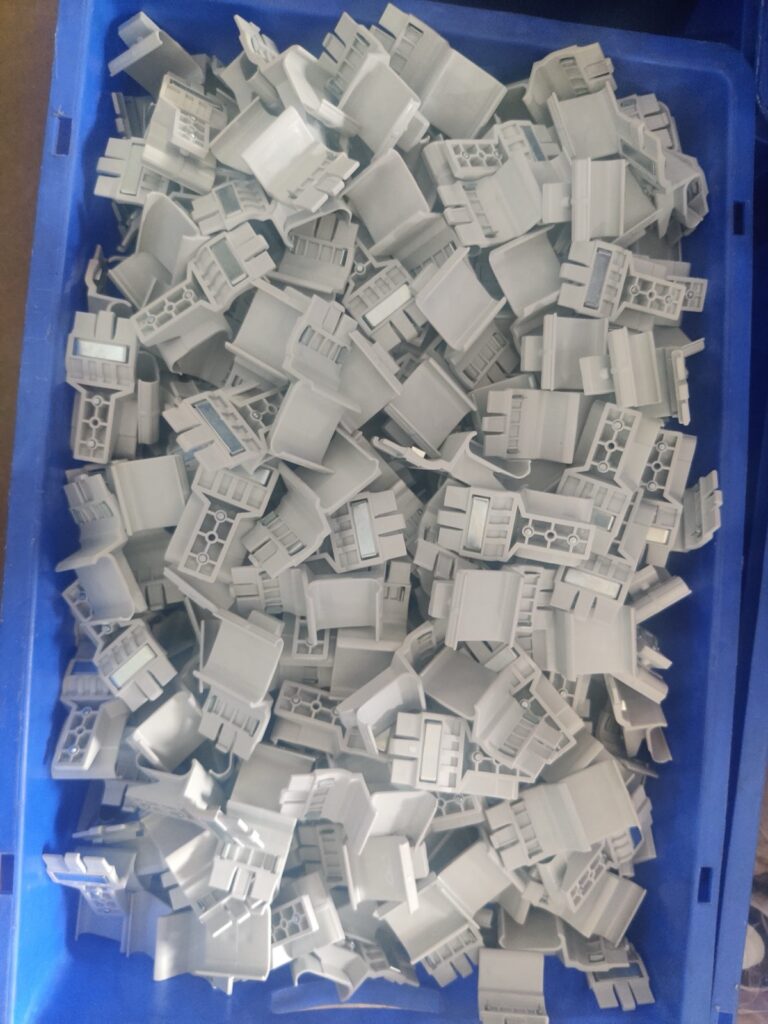
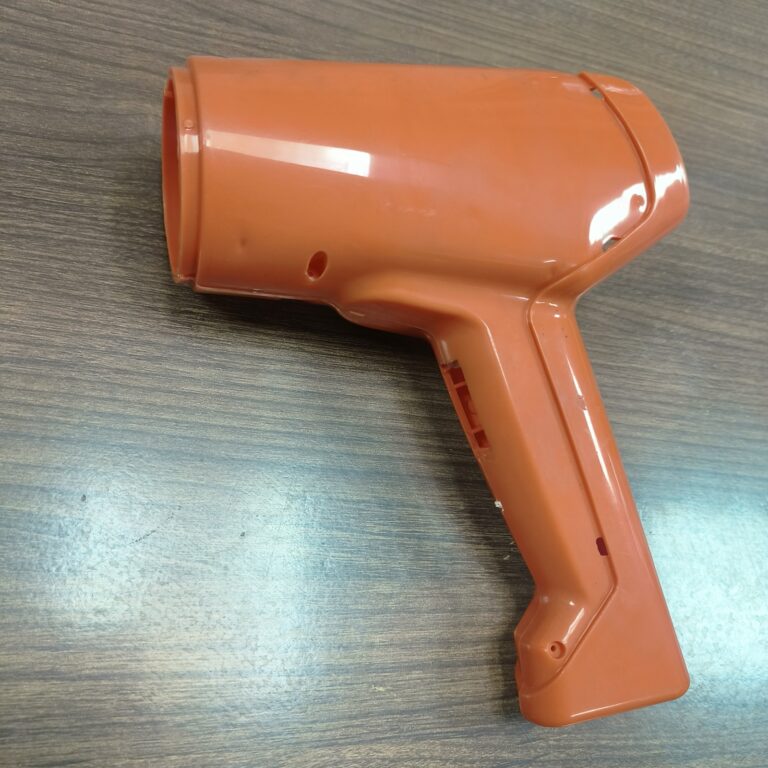














Heavy Fabrication
24000 MT/a
Materials
CS / MS, Alloy steel, Stainless Steel, etc.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
0.8 to 25 mm
Materials
Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Brass, Copper, etc.
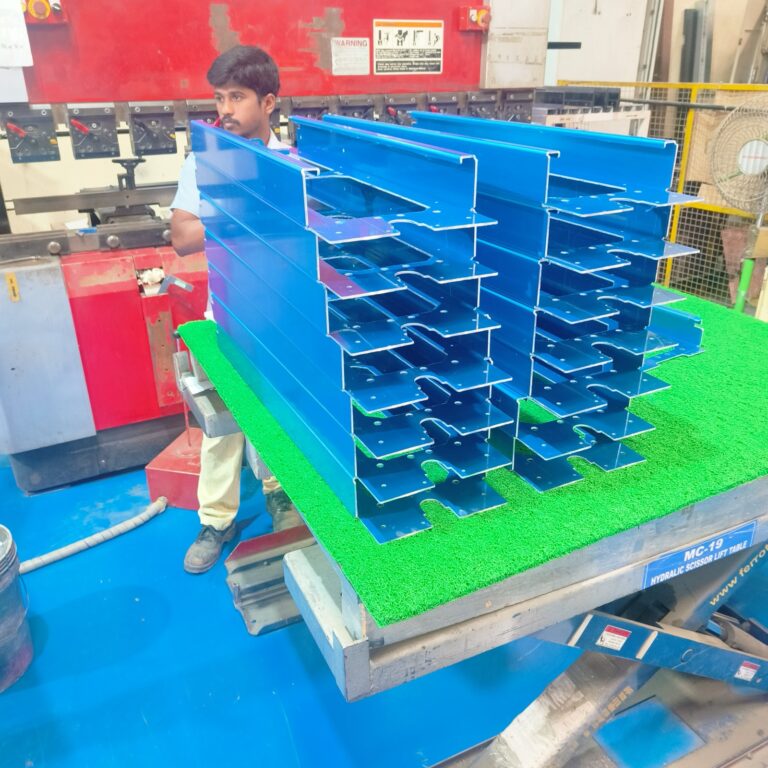
















We'd love to Manufacture for you!
Submit the form below and our representative will be in touch shortly.
LOCATIONS
Global Sales Office
818, Preakness lane, Coppell, Texas, USA – 75019
Registered Office
10-A, First Floor, V.V Complex, Prakash Nagar, Thiruverumbur, Trichy-620013, Tamil Nadu, India.
Operations Office
9/1, Poonthottam Nagar, Ramanandha Nagar, Saravanampatti, Coimbatore-641035, Tamil Nadu, India. ㅤ
Other Locations
- Bhilai
- Chennai
- Texas, USA
















