Forging over machining, when it comes to manufacturing, choosing the right process is crucial for achieving the best results. Forging and machining are two widely used methods, each with its own benefits. However, in many cases, forging has distinct advantages over machining, especially regarding strength, cost, and material efficiency. Let’s explore the advantages of forging and why it might be the better choice for your manufacturing needs.
What is Forging?
Forging is a process where metal is shaped by applying compressive forces, typically using a hammer or press. This process is usually done at high temperatures, which makes the metal more malleable and easier to shape. Forging can produce parts with excellent mechanical properties, making it a preferred choice in many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
What is Machining?
Machining, on the other hand, consist of removing material from a workpiece to produce a desired shape. This is typically done using tools like lathes, mills, or drills. While machining can achieve high precision and intricate details, it often involves more waste and longer production times, making it sometimes less efficient.
The Advantages of Forging Over Machining
1. Superior Durability and Strength
One of the primary advantages of forging is the superior strength of forged parts. During the forging process, the metal’s grain structure is aligned to follow the shape of the part, resulting in a continuous grain flow. Forging over machining increases the mechanical properties of the metal, making the forged parts stronger and more durable than machined parts.
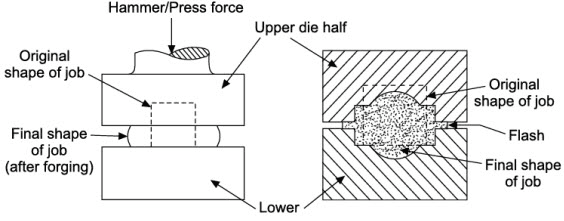
Forged components can withstand higher loads and stresses, making them ideal for complex applications where strength is paramount.
2. Cost-Effective Production
Although the initial setup cost for forging might be higher, the overall cost per part can be significantly lower compared to machining. This is because forging typically requires less material and produces less waste.
Machining removes and discards a considerable amount of the original material, leading to higher costs. In contrast, forging uses almost the entire material, resulting in better material efficiency and lower costs, especially for high-volume production.
3. Enhanced Material Properties
The forging process improves the strength of the material, as well as its toughness and resistance to fatigue and wear. This is due to the work-hardening effect that occurs when the metal is deformed under pressure.
Forged parts are less likely to have internal voids or defects, which can be a concern with machined parts, especially those made from cast blanks. The absence of such defects means forged parts have a longer lifespan and are more reliable in demanding applications.
4. Better Grain Flow
The metal’s grain flow is optimized during forging to follow the part’s contours. This natural alignment of the grain structure contributes to the forged part’s overall strength and toughness.
In contrast, machining cuts through the metal’s grain structure, potentially weakening the material and making it more susceptible to failure under stress.
5. Reduced Lead Times for Large Volumes
Another significant advantage of forging over machining is the potential for reduced lead times when producing large quantities. Once the forging dies are created, the process can be highly automated and efficient, allowing for the rapid production of large parts.
Machining, while precise, often requires more time per part, especially for complex shapes or when multiple setups are needed. This can result in longer lead times and higher labor costs.
6. Improved Fatigue Resistance
Forged parts exhibit better fatigue resistance compared to machined parts. This is particularly important in applications where the component is subjected to cyclic loading or repeated stress, such as automotive or aerospace parts.
The continuous grain flow in forged parts helps to distribute stress more evenly, reducing the chances of fatigue failure.
7. Customization and Versatility
While forging over machining is known for its precision, forging offers significant material selection and customization versatility. One of the most interesting advantages of forging is its versatility to use different raw materials. It can be used with different metals, such as steel, aluminum, and titanium, making it suitable for diverse applications.
Additionally, forging allows for producing complex shapes and geometries that might be challenging or expensive to achieve through machining.
Why Should You Choose Forging Over Machining?
The advantages of forging over machining are clear: superior strength, cost-effectiveness, enhanced material properties, better grain flow, reduced lead times, improved fatigue resistance, and versatility. While machining has its place in manufacturing, especially for high-precision and low-volume parts, forging often provides a more efficient and robust solution for producing high-strength components.
If your industry demands strong, durable, and cost-effective parts, forging over machining might be the ideal choice. At Frigate Die Casting Services, we specialize in high-quality forging processes that deliver exceptional results. Whether you need components for automotive, aerospace, or any other industry, our team has the expertise to meet your needs.
Contact Frigate today to learn more about our forging over machining services and how we can help you achieve the best results for your manufacturing projects.




