Several casting methods are available, including sand casting and investment casting. Both casting methods have a long history, starting in 1838. Although both methods create metal parts by pouring molten metal into molds, they differ. This is why you need to know the right process for your manufacturing needs.
In this article, we will discuss investment casting vs. sand casting so you can decide on the casting manufacturing process for your components.
What is Investment Casting?
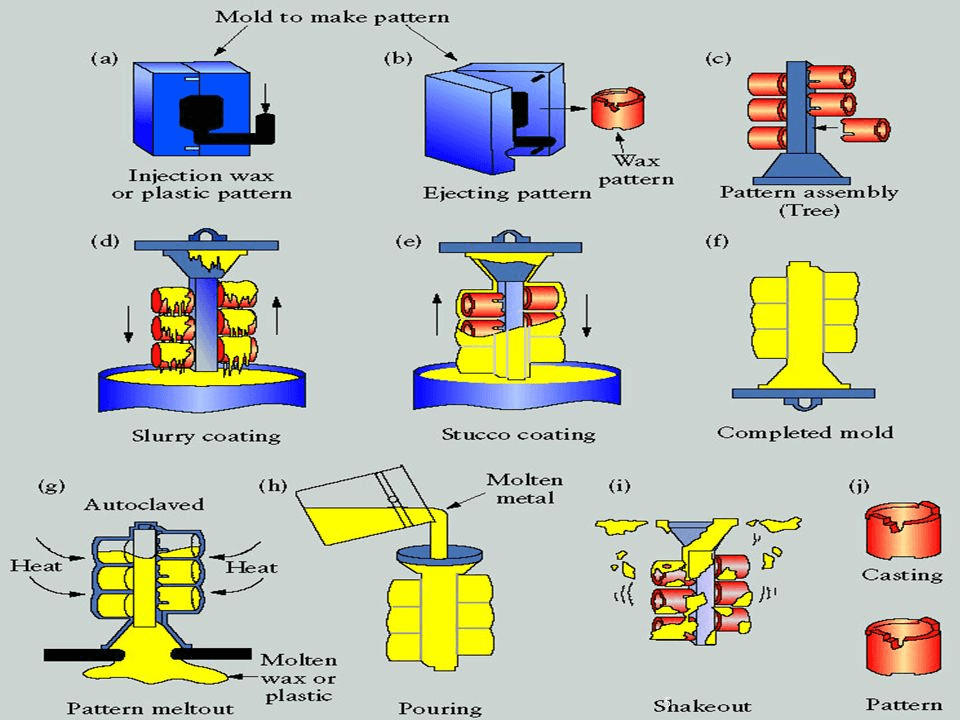
Investment casting is a process in which a pattern creates a void for metal parts. The ceramic shell is created around the wax pattern, and once it has hardened, the wax pattern is removed from the shell. Then, molten metal was poured into the shell, and it solidified. The final investment casting pieces will have a smooth surface and the same shape as the wax patterns. Furthermore, the removed wax can be utilized again.
The following are the benefits of Investment Casting:
- Exceptionally accurate and precise dimensional results.
- Ability to cast both non-ferrous and ferrous metals.
- Provide quality surface finish and detailing.
- It can be used to produce parts with thin walls and complex geometries.
What is Sand Casting?
The sand casting process is suitable for brass, iron, steel, and alloys. In this process, a sand mold is created to make the desired shape. Most of the time, sand is mixed with the clay and moistened with water to increase the mold’s strength. Sand molds always have two halves, which are quickly fastened during the casting process. One drawback of sand casting is that the molds can be used only once, and sand can be reused.
Here are some of the advantages of choosing sand casting:
- Ability to cast components with a wide range of materials with some or no process change.
- Lower wastage compared to other methods.
- A great option for prototyping and small batches.
- It can produce parts weighing grams to tons.

Investment Casting vs Sand Casting
Investment casting and sand casting are both methods that have experienced considerable improvement over the years, whether in terms of the quantity of metal cast, the reduction of extensive machine requirements, or finishing. However, they both are different in multiple ways; let’s explore those differences:
Cost
The cost of the investment casting process is high compared to the sand casting process. The reason is that investment casting is complex and includes a lot of preparation before starting to cast components.
Weight of casted components
Investment casting can manufacture components smaller than 1lb, while sand casting can not always produce small and complex parts. Investment casting also has limitations on weight and size. The mold-handling equipment at the plant affects the product’s weight.
Surface Finish
Another big difference between sand casting and investment casting is surface polish. When used with an aluminum template, investment casting can produce finished parts with low tolerances and smooth surfaces. The casting blank is the last component to be delivered after the sprue gate is removed and shot blasting is done. The finished object must be released in sand casting by splitting the mold apart. A dividing line will, therefore, be left outside the finished section. The abrasive sand will also make the surface of the completed cast parts similarly rough. Therefore, more money and effort will be spent on secondary machining to remove the parting line and provide a smoother surface.
Ease of Design
The investment casting technique uses liquid slurry to make a ceramic shell mold. This allows for nearly infinite shape possibilities for the parts produced, providing engineers with great design freedom to incorporate delicate details and complex shapes. Sand casting pieces typically need to be curved or tapered (with draft angles) to emerge from the sand more easily and with less friction. Making pieces with internal cavities or voids presents another difficulty for sand casting. Cores must be appropriately formed and placed inside the mold to build the inside of the part during sand casting. Using multiple cores can occasionally be necessary, and it takes time to make and secure them inside each mold.
Cycle Time
Although they have rather different cycle periods, investment casting and sand casting can reach large volumes. It could take a while to make sand casting and smooth out the uneven surface another time. Investment casting, on the other hand, offers a speedy shot cycle time and production procedure without any after-process products.
What should you choose, investment casting vs sand casting?
Sand casting does not permit pattern undercuts, whereas investment casting does. This is one of investment casting’s main advantages. In investment casting, the pattern is evaporated by heat, while in sand casting, the design must be extracted from the sand after it has been packed. Investment casting often results in a better surface polish and makes creating thinner sections and hollow castings easier. However, investment casting can have a lower success rate compared to sand casting due to the additional processes and potential for errors. It is also a more costly and time-consuming technique.
Conclusion
Investment casting vs. sand casting are both efficient methods for casting components. It completely depends upon your manufacturing needs to choose the right process.
Are you also looking for investment casting and sand casting for your business? Contact an expert at Frigate or request a quote. We can help you find a custom solution for your manufacturing project.