Hot forging is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry, especially when producing high-strength components that require durability and precision. Whether it’s automotive parts, industrial machinery, or aerospace components, hot forging is pivotal in shaping the materials that keep our world moving. But what exactly is hot forging, and why is it so essential? This blog will delve into the intricacies of hot forging, explore its industrial applications, and highlight why it’s a go-to process for many manufacturers.
What is Hot Forging?
Hot forging is when a piece of metal is heated to a temperature above its recrystallization point and then deformed to achieve a desired shape. This process alters the metal’s microstructure, enhancing its properties, such as flexibility, strength, and toughness. The heat allows the metal to flow more easily, reducing the likelihood of cracks and improving the final product’s quality.
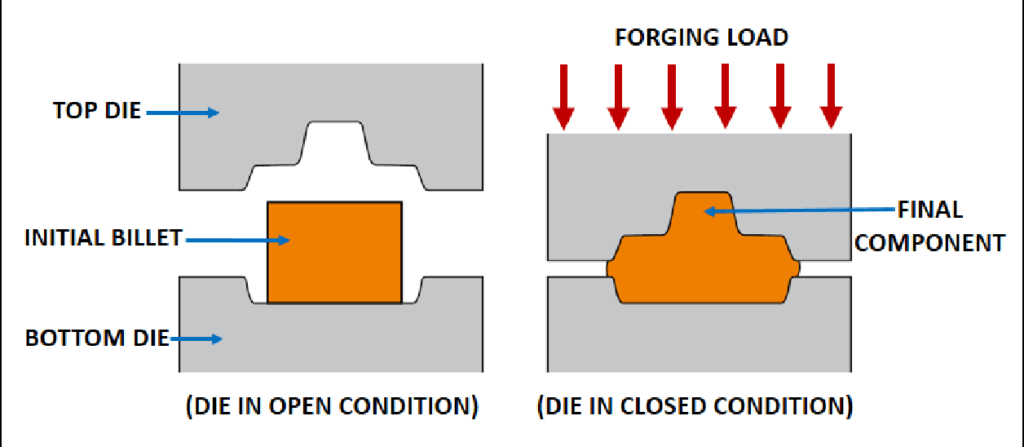
Key Points of Hot Forging
- Temperature: The metal is heated above its recrystallization temperature, typically between 1,500°F and 2,500°F, depending on the material.
- Deformation: The heated metal is then deformed using a die or hammer, shaping it into the required form.
- Microstructure Enhancement: The process refines the grain structure, improving mechanical properties.
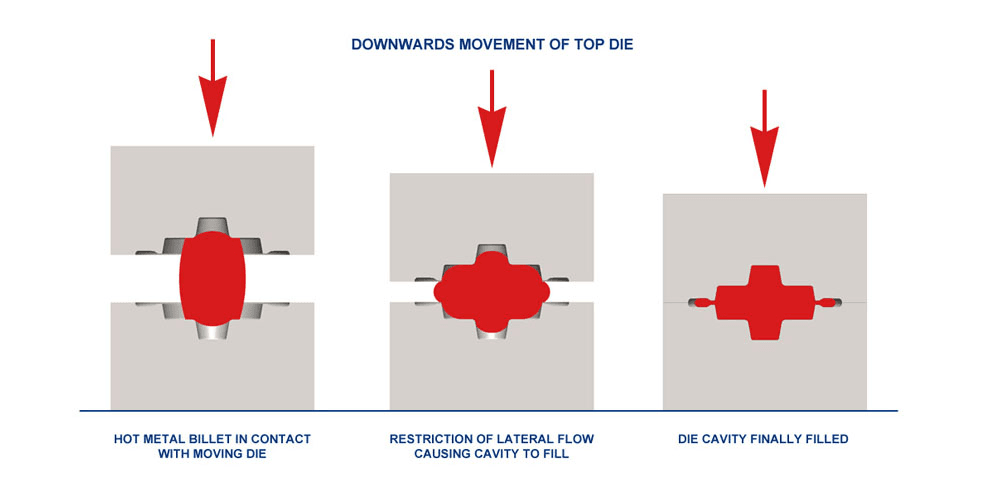
How Hot Forging Works?
The hot forging process can be broken down into several key steps, each critical to achieving a high-quality final product:
- Heating the Metal: The metal workpiece is heated to the required temperature. The exact temperature depends on the material being forged, but it must be high enough to allow for plastic deformation without cracking.
- Deformation: Once heated, the metal is placed in a forging die or under a hammer. The applied force causes the metal to flow into the desired shape. This step is where the actual forming of the part occurs.
- Cooling: After the metal has been shaped, it is cooled naturally in the air or a controlled environment. The cooling rate can affect the properties of the metal, such as hardness and toughness.
- Finishing: Any excess material, known as flash, is trimmed away, and the part may undergo additional machining or heat treatment processes to achieve the desired specifications.
Benefits of Hot Forging
- Increased Strength: The refined grain structure and uniformity achieved through hot forging result in a stronger final product.
- Improved Ductility: Hot forging enhances the material’s ability to deform without fracturing, making it more durable.
- Cost-Effective: While the initial setup for hot forging can be expensive, it is highly efficient for large-scale production runs, reducing the overall cost per part.
- Customizability: Hot forging allows for the production of complex shapes and designs tailored to specific industrial needs.
- High Production Rates: The process is suitable for mass production, making it ideal for industries requiring large parts.
- Consistency: This type of forging ensures uniformity and consistency in the mechanical properties of the parts, which is essential for maintaining quality in industrial applications.
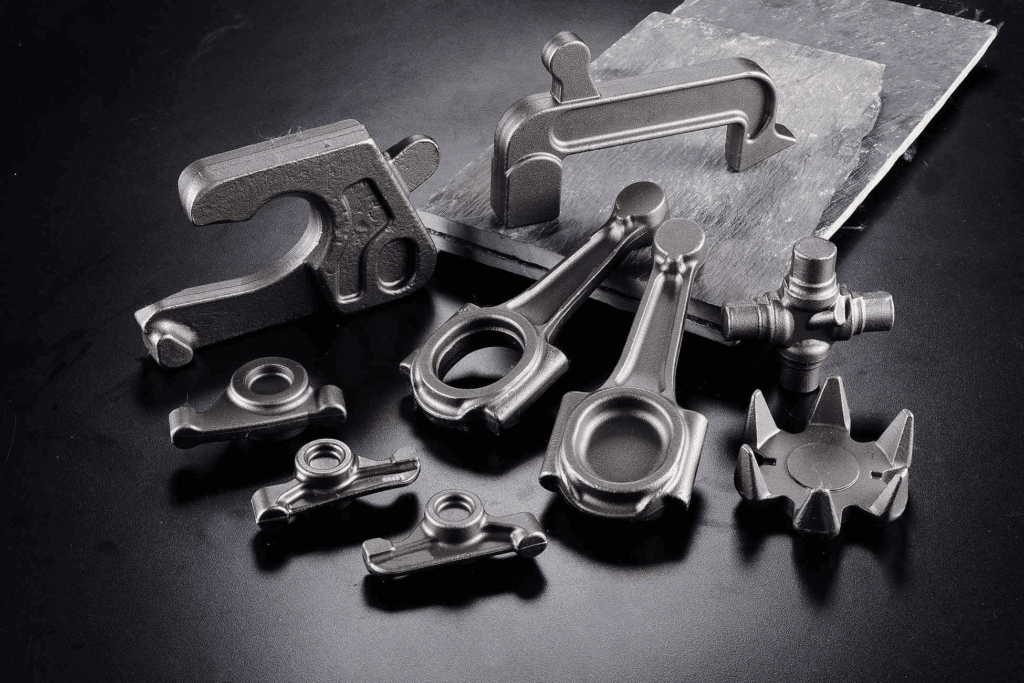
Industrial Applications of Hot Forging
Hot forging is used across various industries because it produces parts with superior mechanical properties. Some of the most common applications include:
Automotive Industry
It is widely used in the automotive industry to manufacture components such as crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, and axles. These components must withstand high stress and fatigue, making hot forging the ideal process due to its enhanced strength and toughness.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry values hot forging to produce critical components like turbine blades, landing gear, and structural parts. These parts require a high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional durability, which hot forging delivers.
Oil and Gas Industry
Hot forging produces parts like valves, flanges, and fittings that can endure extreme temperatures and pressures. The reliability and integrity of these components are crucial, making hot forging the preferred manufacturing method.
Heavy Machinery
Components for heavy machinery, such as hydraulic presses, mining equipment, and construction vehicles, are often forged hot. The process ensures these parts can handle the demanding conditions they are exposed to in the field.
Power Generation
Turbine shafts, generator rotors, and other critical parts used in power plants are often hot-forged to ensure they can withstand the high operational stresses they encounter.
Why Choose Hot Forging?
Given the demanding requirements of modern industries, hot forging stands out as a preferred manufacturing method for producing high-quality, durable parts. The process not only enhances the mechanical properties of the materials but also allows for the creation of complex shapes that might be difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
- Material Selection: The type of material being forged plays a significant role in identifying the final properties of the component. Common materials used in this type of forging include steel, aluminum, titanium, and nickel-based alloys.
- Tooling and Equipment: The quality of the dies and hammers used in hot forging directly impacts the quality and precision of the forged components. Advanced tooling can significantly improve efficiency and reduce waste.
- Process Control: Maintaining the correct temperature and deformation rates is crucial for achieving the desired properties in the forged part. Precision in these parameters ensures consistent and reliable results.
Conclusion
Hot forging is an indispensable process in the manufacturing world. It offers unmatched strength, durability, and precision for a wide range of industrial applications. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or heavy machinery industry, hot forging provides the reliability and performance needed to meet the most demanding requirements.
If you’re looking for a trusted partner in hot forging, Frigate Forging Services is here to help. With years of experience and state-of-the-art equipment, we can deliver the high-quality components your industry demands. Contact Frigate today to learn more about how our hot forging services can meet your specific needs.



